
Home | About Jay Hochman -Pediatric Gastroenterology Blog | Archives
February 19, 2026 7:00 am
RS Dalal et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2026; 24: 255-257. One-Year Comparative Effectiveness and Safety of Upadacitinib vs Risankizumab for Crohn’s Disease
This was a retrospective single-center study (n=219) assessing upadacitinib (n=67) or risankizumab (n=152) for active Crohn’s disease (CD). Treatment initiation as post-operative prevention or for non-CD indication were excluded.
**The patients receiving upadacitinib were generally younger, had more anti-TNF/ustekinumab failures, higher CRPs, and higher HBSs compared to risankizumab-treated patients.
Key findings:

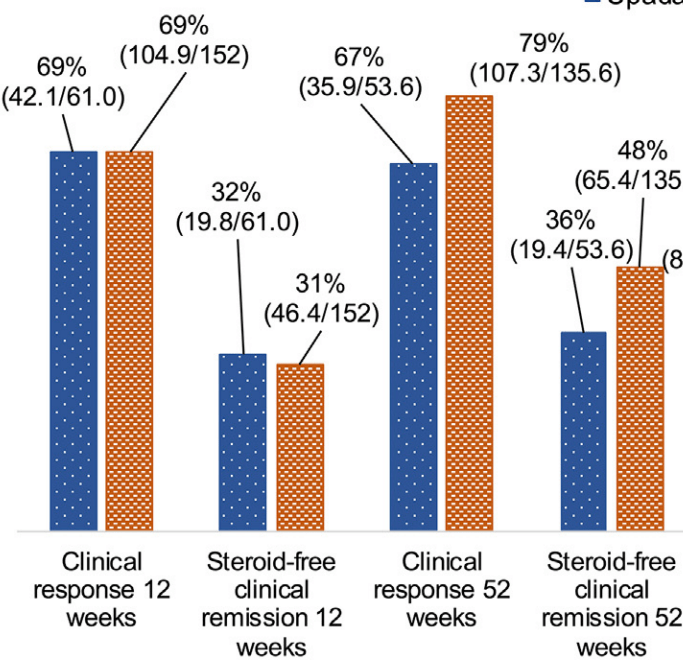
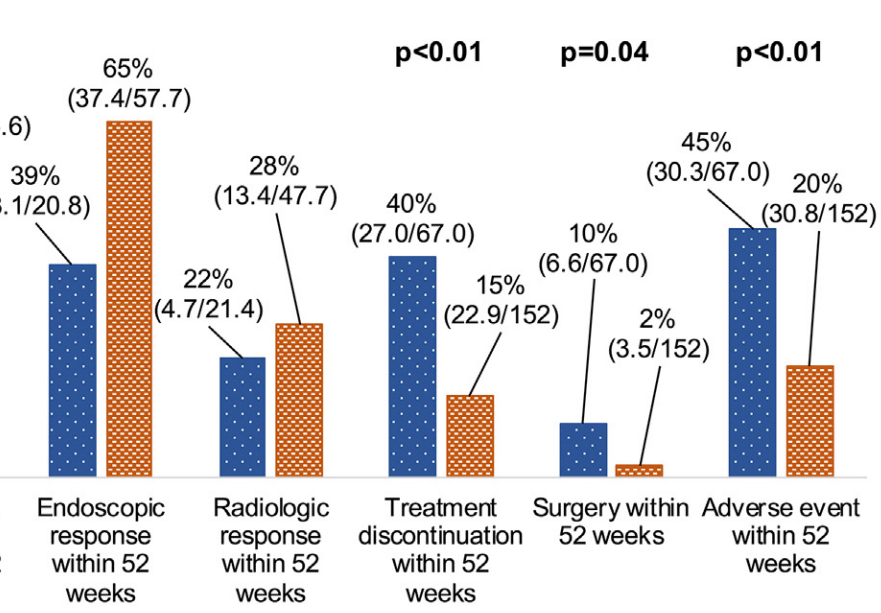
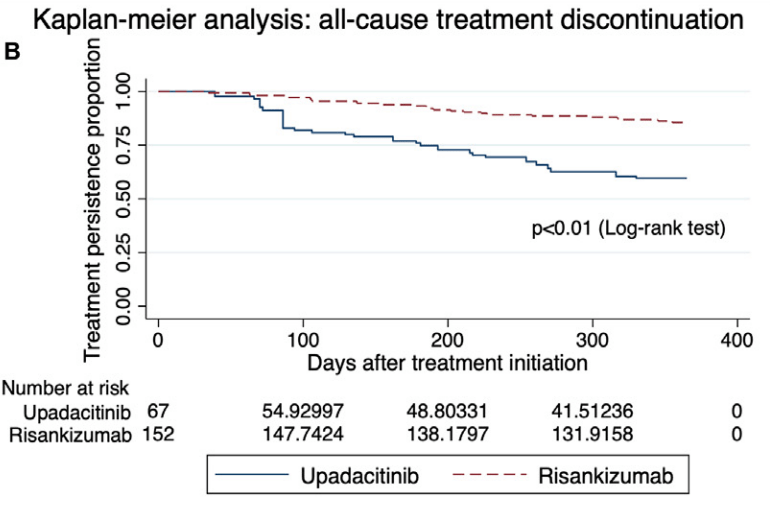
My take: While this study favors risankizumab over upadacitinib, most of the outcomes were fairly similar. Risankizumab may have better long-term durability. However, the observational design limits the conclusions, particularly as the upadactinib-treated patients appeared to be more refractory at baseline. A prospective head-to-head study would be more definitive.
Related blog posts:
Posted by gutsandgrowth
Categories: Pediatric Gastroenterology Intestinal Disorder
Tags:
Mobile Site | Full Site
Get a free blog at WordPress.com Theme: WordPress Mobile Edition by Alex King.