SP Ashcroft et al. Cell Metabolism 2024; https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2023.12.008. Open Access! Exercise induces tissue-specific adaptations to enhance cardiometabolic health
This is a 23 page review with 395 references.
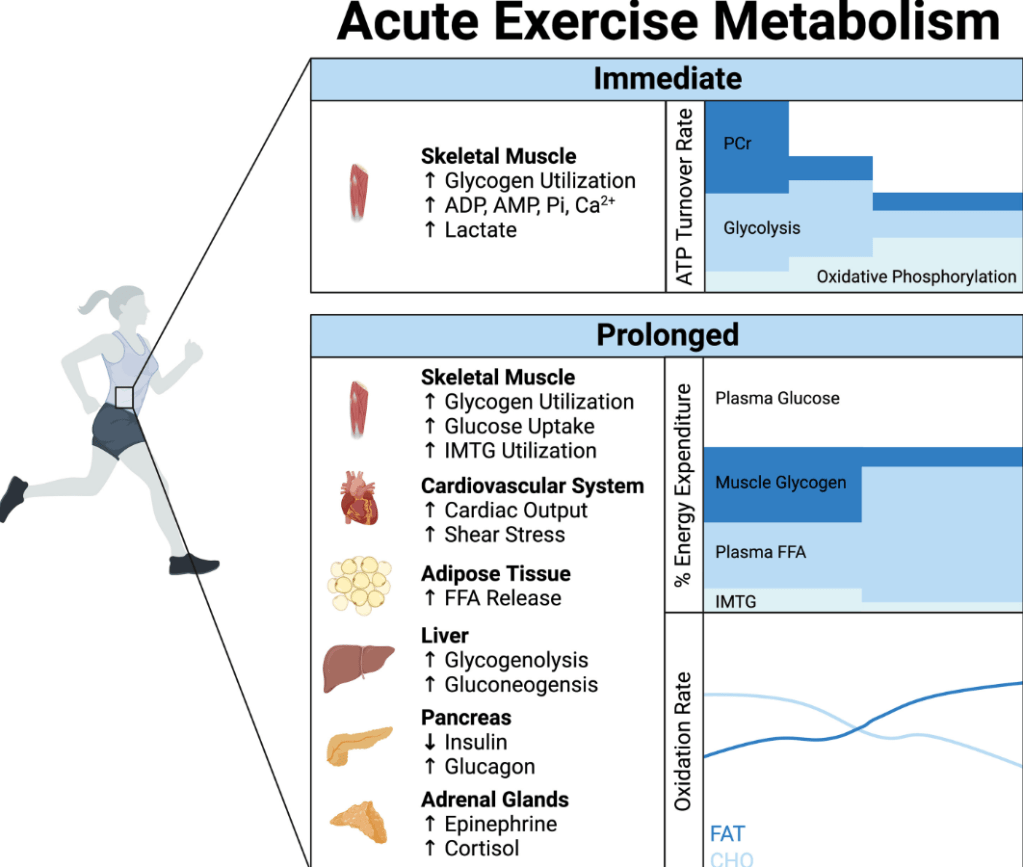
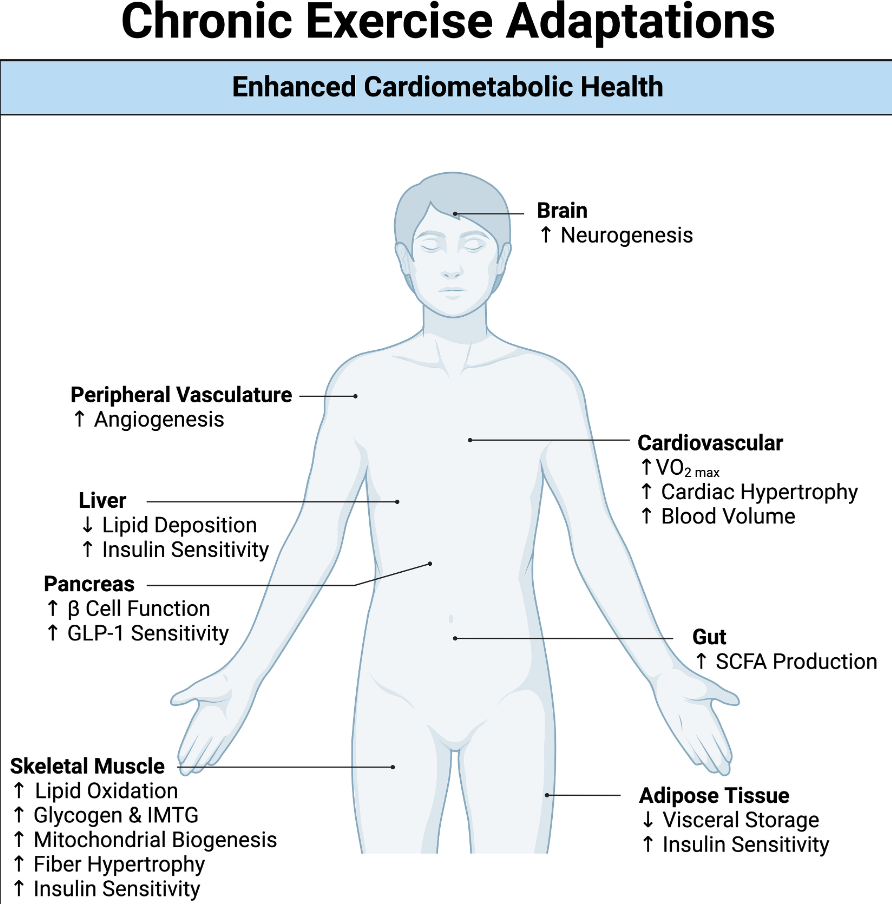
“The risk associated with multiple cancers, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and all-cause mortality is decreased in individuals who meet the current recommendations for physical activity…Over time, the associated metabolic stress of each individual exercise bout provides the basis for long-term adaptations across tissues, including the cardiovascular system, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, pancreas, gut, and brain. Therefore, regular exercise is associated with a plethora of benefits throughout the whole body, including improved cardiorespiratory fitness, physical function, and glycemic control. Overall, we summarize the exercise-induced adaptations that occur within multiple tissues and how they converge to ultimately improve cardiometabolic health.”
Related blog posts:
