From UCSD 4/28/25: Children with Liver Disease Face Dramatically Higher Risk of Early Death (via Jeff Schwimmer’s X feed)
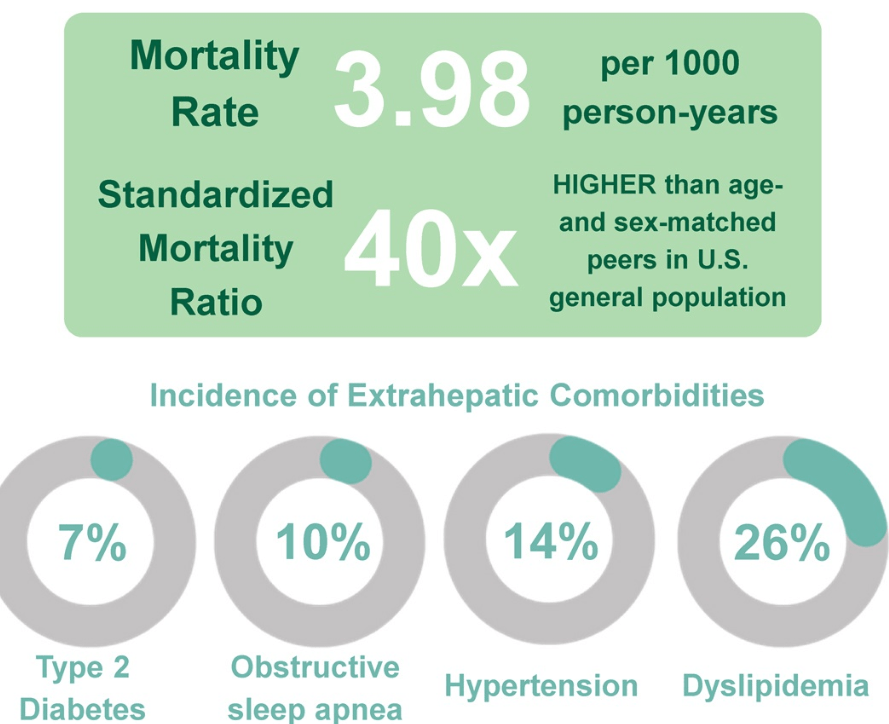
The findings, published April 22, 2025 in Hepatology, the scientific journal of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, come from the Longitudinal InVestigation Evaluating Results of Steatosis (LIVERS) study, which followed 1,096 children over an average of 8.5 years. Nearly half of all deaths in the cohort were liver-related, and the overall mortality rate was 40 times higher than that of similar peers in the general U.S. population...
The retrospective cohort study used medical records and National Death Index data to follow children ages 2 to 18 who were diagnosed with MASLD between 2000 and 2017. Over an average of 8.5 years of follow-up, 3.4% of children had died…
In addition to the risk of early death, many children in the study developed serious health problems while still in their teens or twenties. These included high blood pressure (14%), obstructive sleep apnea (9.5%) and type 2 diabetes (7.3%). Problems with blood fats, such as high triglycerides or low HDL, were even more common — making dyslipidemia, the presence of abnormal levels of fats (lipids) in the blood, the most frequent complication overall.
Link to study: JB Scwimmer et al Hepatology ():10.1097/HEP.0000000000001357. Long-term mortality and extrahepatic outcomes in 1,096 children with MASLD: A retrospective cohort study
My take: Since this was a retrospective single center study, the severity of the findings may be different with a more-representative national cohort. Nevertheless, this study shows that MASLD has serious consequences including premature death and numerous comorbidities.
Related article: J Panganiban et al. Obesity Pillars 2025: 14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obpill.2025.100164. Open Access! Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in children with obesity: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) and expert joint perspective 2025. This Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Expert Joint Perspective is a comprehensive review (~28 pages) of steatotic liver disease (SLD), metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) in children with obesity.
Related blog posts:
- Key Insights on MASLD from Dr. Marialena Mouzaki
- Semaglutide in Adolescent Obesity
- Pharmacological Management of Pediatric Steatotic Liver Disease
- Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) & Uptick in GLP1 Use
- AASLD Practice Changes for Metabolic Liver Disease in 2024
- Bariatric Surgery Declines as GLP-1 Medications Rise
- Survodutide, Dual Glucagon Receptor/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, for MASH (Phase II Trial)
- Resmetirom (Rezdiffra) -FDA Approved for MASH with Moderate to Advanced Fibrosis
- What’s More Important for Health: Exercise or Weight loss?
- Why Exercise is Good For Health
