L Ji et al. NEJM 2025; 392: 2215-2225. Once-Weekly Mazdutide in Chinese Adults with Obesity or Overweight
This study from China enrolled young participants (mean age 34 yrs) and lower BMI (mean 31.1) than in similar studies of other GLP1 RAs and GLP 1 RA/GIP dual agonists. However, there was a high prevalence of dyslipidemia (62.3%), MAFLD (48.9%), hyperuricemia (40.2%), and hypertension (22.8%).
Key findings:


- At week 48, the mean percentage change in body weight from baseline was –11.00% in the 4-mg mazdutide group, –14.01% in the 6-mg mazdutide group, and 0.30% in the placebo group

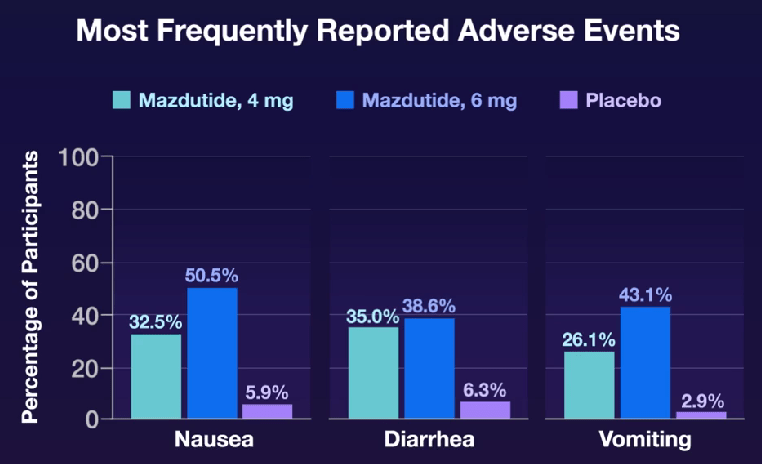
My take: Mazdutide resulted in significant weight loss along with improvements in cardiometabolic measures. This study shows beneficial effects in a younger cohort with significant cardiometabolic disease. Improvements in younger populations is likely to result in more substantial effects on outcomes than improvement in older cohorts.
Related blog posts:
- Head-to-Head: Tirzepatide Outperforms Semaglutide
- Survodutide, Dual Glucagon Receptor/GLP-1 Receptor Agonist, for MASH (Phase II Trial)
- Key Insights on MASLD from Dr. Marialena Mouzaki
- Lifetime Health Effects and Cost-Effectiveness of Tirzepatide and Semaglutide in US Adults
- Tirzepatide: Breakthrough in Obesity and Diabetes Management (SURMOUNT-1 Study at 3 years)
- Tirzepatide for Metabolic Dysfunction–Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) & Uptick in GLP1 Use
