J Gao et al. Gastroenterology. 206; 170:132 – 147. Open Access! Low Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols Diet Improves Colonic Barrier Function and Mast Cell Activation in Patients With Diarrhea-Predominant Irritable Bowel Syndrome: A Mechanistic Trial
Background: “Mechanisms by which fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) drive pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are not well understood.”
Methods: 42 patients with “Rome IV diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D) underwent barrier function evaluation pre- and post-LFD along with assessment of mast cell number and activation profile. Finally, fecal supernatants (FS) were administered intracolonically to wild-type mice with and without pharmacologic inhibition, toll-like receptor 4 (tlr4)–/– mice, and mast cell-deficient mice with/without mast cell reconstitution.”
Key findings:
This is a highly technical study and would recommend reviewing the findings directly (open access article).
To summarize:
- “Patients with IBS-D had significant improvement in colonic barrier structure and function, mast cell number, and levels of mast cell mediators post-LFD (low FODMAP diet). The magnitude of physiological changes did not correlate with the magnitude of clinical response.”
- “This study showed the complex interplay among food, microbiome, local immune activation, and epithelial physiology in IBS by demonstrating that FODMAPs increase fecal lipopolysaccharide levels, which activates colonic mast cells to causes barrier dysfunction in diarrhea-predominant IBS.”
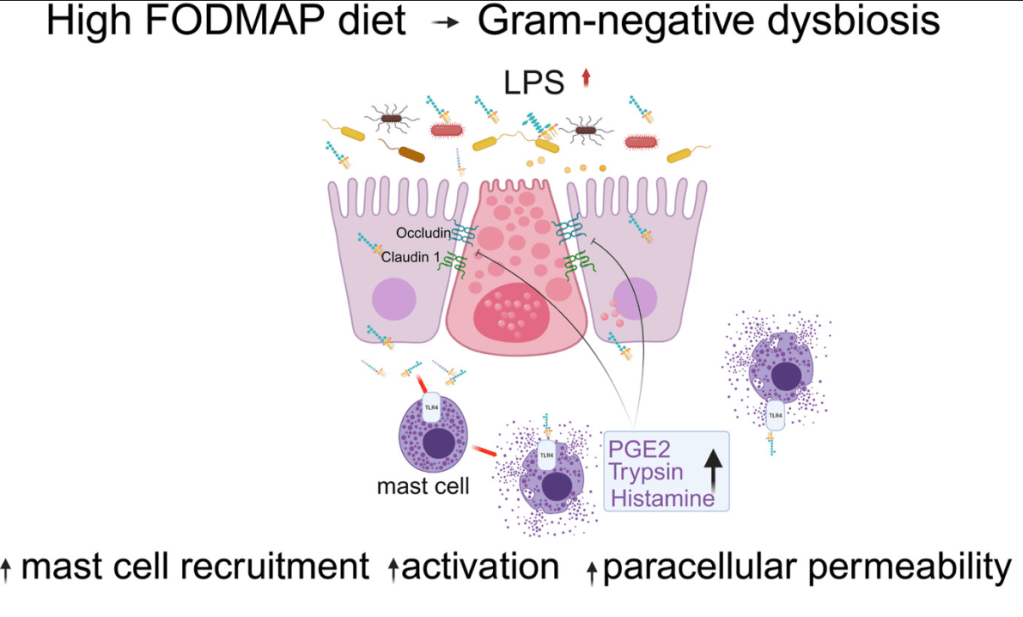
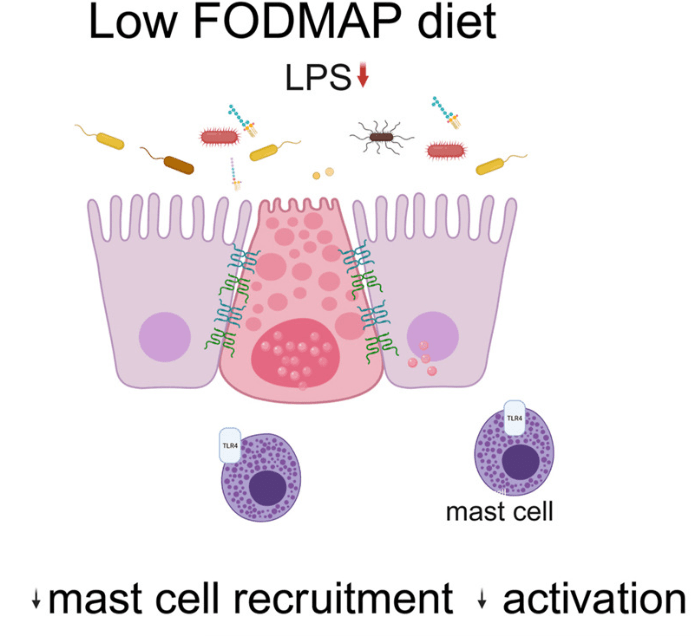
My take: By understanding the GI effects of a low FODMAP diet in patients with IBS-D more precisely, it may improve dietary approaches as well as other treatments like mast cell stabilizers.
Related blog posts:
- Pilot Study: Mediterranean Diet vs Low FODMAP for Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Does a Less Restrictive Low FODMAP Diet Work?
- Which FODMAPs are Most Difficult to Reintroduce in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Treatment of Refractory Celiac Symptoms with a Low FODMAP Diet
- Differential Microbiome Effects of Prebiotics and low FODMAPs
- Fructans and FODMAPs in Children with Irritable Bowel Syndrome
