EW Hall et al. J Pediatr 2023; 258: 113409. Open Access PDF! Cost-Effectiveness of Strategies to Identify Children with Perinatally Acquired Hepatitis C Infection
In this study, the authors modeled three strategies for screening for Hepatitis C infection in children and compared to baseline testing (current approach): : anti-HCV with reflex to HCV RNA at 18 months among children known to be perinatally exposed.
New strategies:
- #1: HCV RNA testing at 2-6 months among infants known to be perinatally exposed
- #2 universal anti-HCV with reflex to HCV RNA at 18 months among all children
- #3 universal HCV RNA testing at 2-6 months among all infants
Key findings:
- Each of the 3 alternative testing strategies resulted in an increased number of children tested and improved health outcomes. HCV RNA testing at 2-6 months (test strategy 1) was cost-saving and resulted in a population-level difference in cost of $469 671.
- More testing in each of the universal comparison strategies resulted in increased QALYs, but also over $38 million to over $129 million
In the discussion, the authors elaborate on why testing at 2-6 months is now the best approach:
- “Factors driving these results include pediatric loss to follow up at older ages, high attendance at well-child visits in the first 6 months of life, and highly sensitive nucleic acid testing with reliable results starting at age 2 months.”
- “One study assessing >150 000 children at 2 health networks spanning 20 states determined children rarely missed 2-month, 4-month, and 6-month well-care visits, whereas 15-month and 18-month visits were attended by less than one-half of publicly insured children”
- Current recommendations are for all pregnant women receive HCV screening, though currently it is below 50%. The universal testing strategy becomes more cost prohibitive as more women receive HCV testing in pregnancy
The CDC has undertaken a review and is likely to implement the 2-6 month old testing strategy as a recommendation. The authors of this study are involved in this process. A slide set reviewing the draft recommendations from 12/6/22:
Link 40 Slides: Overview of draft CDC recommendations for perinatal hepatitis C testing
Some selected slides:



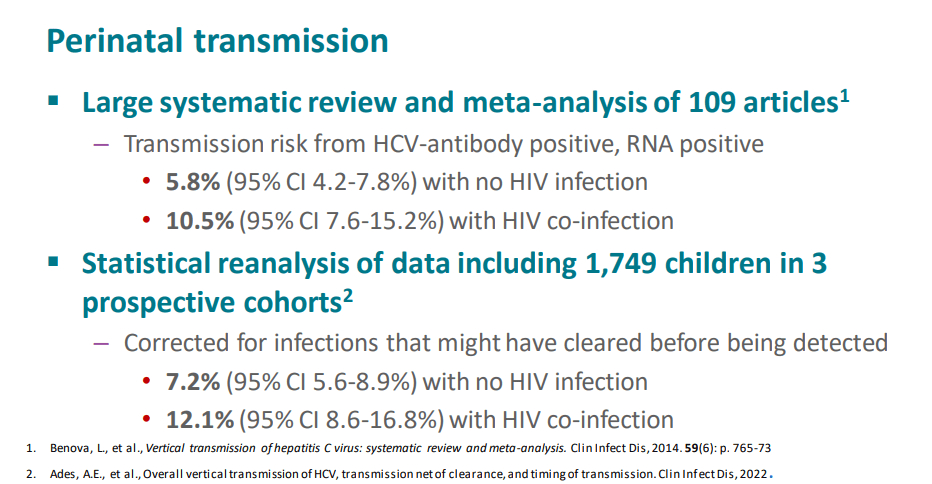
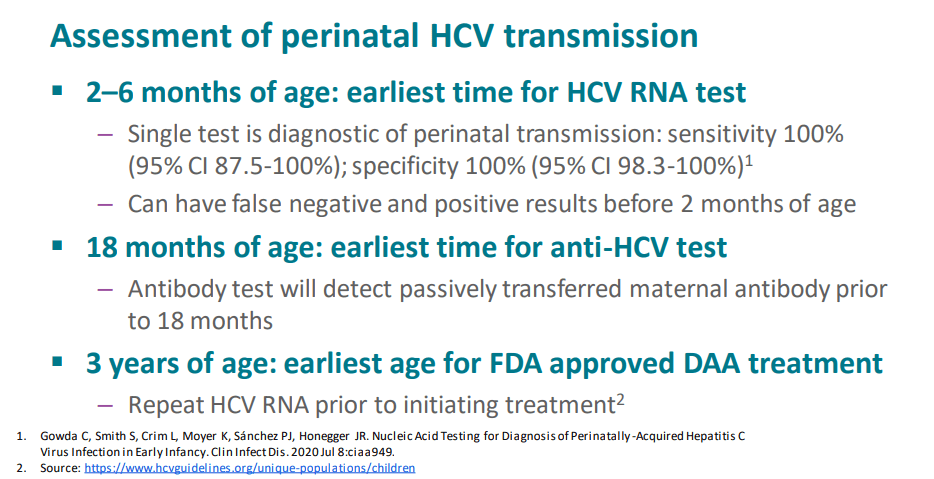
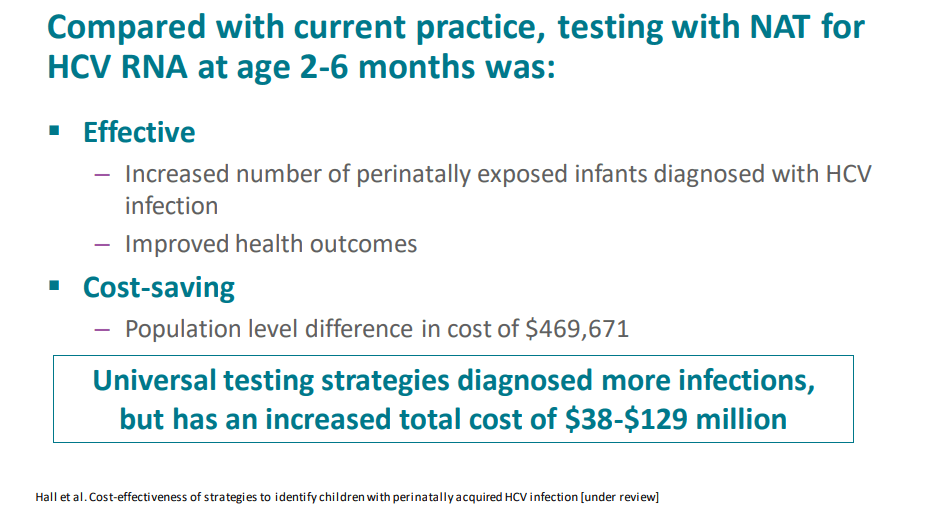



My take (borrowed from authors): Testing of perinatally exposed infants at age 2-6 months with a single HCV RNA test will reduce costs and improve health outcomes.
Related blog posts:
