L Laine et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2024; 22: 2211-2220. Open Access! Vonoprazan is Efficacious for Treatment of Heartburn in Non-erosive Reflux Disease: A Randomized Trial
This was a randomized trial (n=772) in patients diagnosed with non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) comparing vonoprazan (10 mg and 20 mg) versus placebo for heartburn relief. Reflux was NOT confirmed with ambulatory pH monitoring.
Key findings:
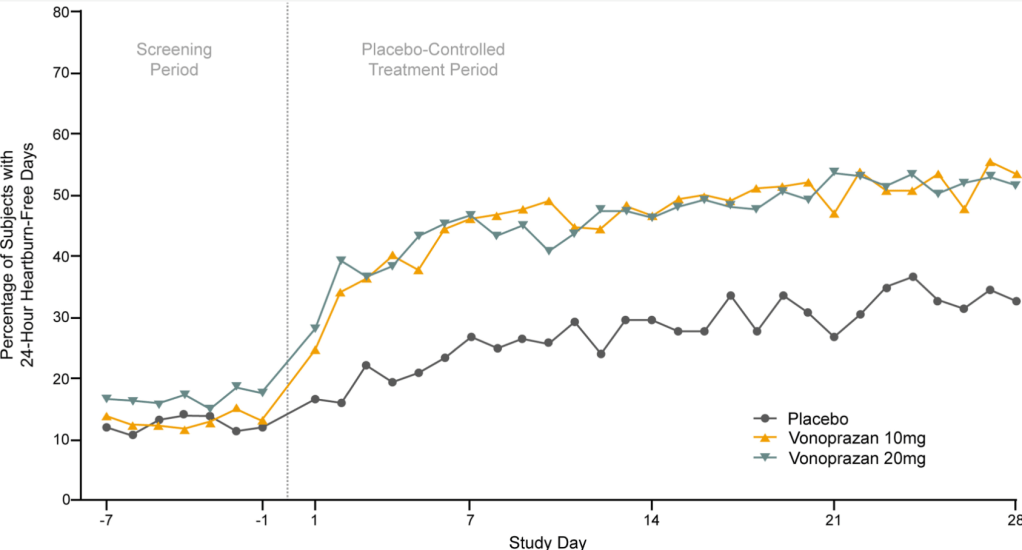
- The percentage of 24-hour heartburn-free days was 27.7% for placebo vs 44.8% for vonoprazan 10 mg (P < .0001) and 44.4% for vonoprazan 20 mg ( P < .0001).
- The results were similar between both doses of vonoprazan
- The benefit of vonoprazan appeared to begin as early as the first day of therapy. Treatment effect persisted after the initial 4-week placebo-controlled period throughout the 20-week extension period.
- In a post-hoc analysis, there was a very small response in patients without prior PPI response compared to placebo: There was a possible trend to fewer (7%–9%) 24-hour heartburn-free days with vonoprazan in those without prior PPI response
Discussion points: “Post hoc analysis raised the possibility that patients who previously had not responded to PPIs may have a somewhat lower response to vonoprazan. This is not unexpected, given that patients not responding to PPIs are less likely to have heartburn due to acid reflux” and more likely to have functional heartburn. The treatment effect of vonoprazan was less clear in the subgroup of patients with NERD and with severe heartburn “It is conceivable this group included a higher proportion of subjects with functional heartburn, a condition that is generally not responsive to acid inhibition.”
My take: Vonoprazan is more effective than placebo for heartburn in patients with NERD. However, the absence of definite improvement in the patients with lack of prior PPI response along with the lack of difference between the 10 mg and 20 mg vonoprazan groups indicates that this therapy should NOT be used routinely in patients with NERD in the absence of documented reflux based on ambulatory pH studies.
Related blog posts:
- Is Vonoprazan Better Than Intravenous PPIs for High-Risk Peptic Ulcers?
- Improved Efficacy with Vonoprazan for Severe Esophagitis
- Differentiating NERD from Functional Heartburn
- Regurgitation harder to treat than heartburn, especially for NERDs
- Does Nonerosive Reflux Increase the Risk of Esophageal Cancer?
- What’s Going on With Refractory Heartburn?
- How Many Kids with Reflux Actually Have Reflux?
- Why Vonoprazan Is More Effective For Erosive Esophagitis Than a Proton Pump Inhibitor
- Understanding FDA Approval of Vonoprazan-Based Therapies for Helicobacter Pylori
- Safety and Efficacy of Potassium Competitive Acid Blockers (3 Studies)
- All Bleeding Stops (part 2)
- All bleeding stops
