WTGarvey et al. N Engl J Med 2025;393:635-647. Coadministered Cagrilintide and Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity
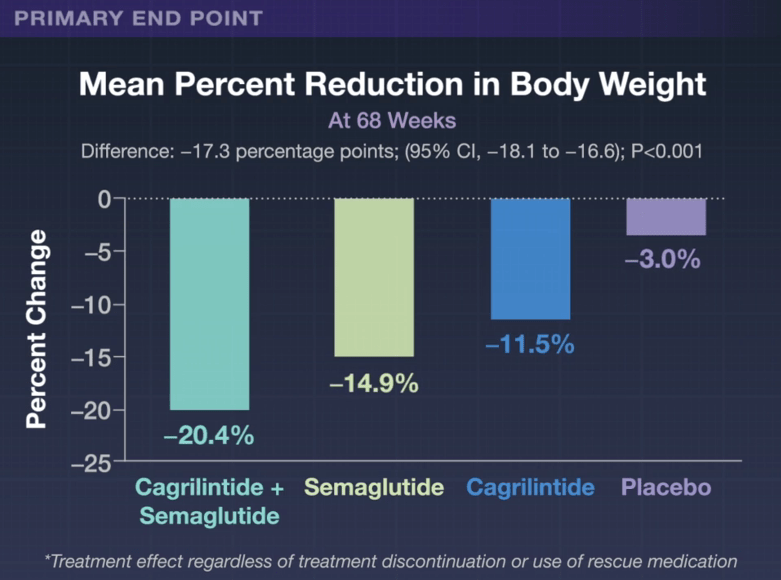
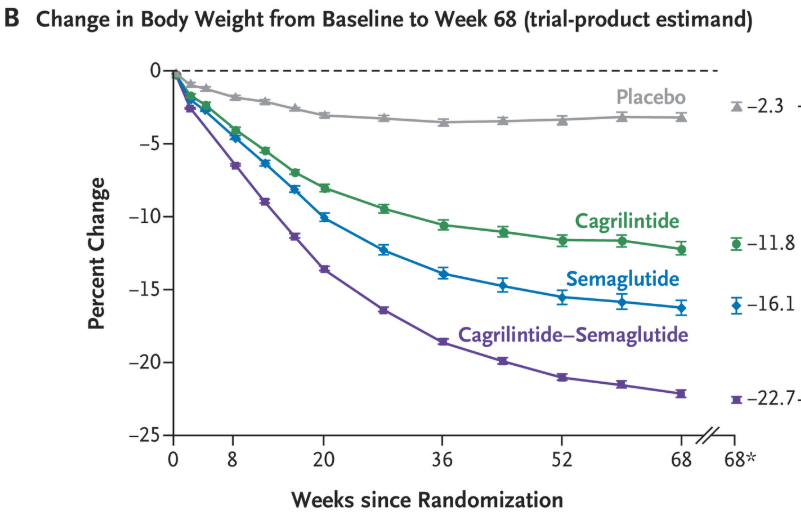
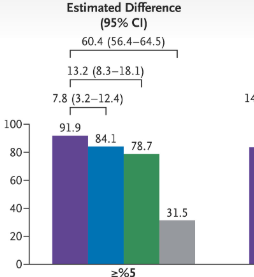
This phase 3a, 68-week, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled and active-controlled trial (REDEFINE 1) examined the efficacy of the combination of Cagrilintide and Semaglutide (known as CagriSema). Patients had a body-mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher or a BMI of 27 or higher with at least one obesity-related complication. The combination druge was delivered as a fixed-dose in a single-dose, single-use pen device. 6.1% of trial participants had BMI <30.


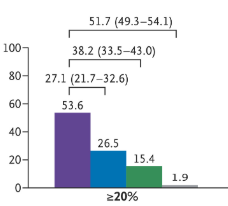
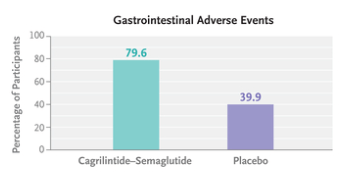
- “Gastrointestinal adverse events (affecting 79.6% in the cagrilintide–semaglutide group and 39.9% in the placebo group), including nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, or abdominal pain, were mainly transient and mild-to-moderate in severity.”
- “Although 57.4% of the participants assigned to cagrilintide–semaglutide were receiving the maximum dose at 68 weeks, 74.7% had received the maximum dose at some point after randomization…doses below the target might be highly effective for some patients and that dose reductions based on the clinical judgment…may be appropriate.”
This same issue also examined the use of this combination in patients with type 2 diabetes (REDEFINE 2). in this study with 1206 patients, “the estimated mean change in body weight from baseline to week 68 was −13.7% in the cagrilintide–semaglutide group and −3.4% in the placebo group.”
The editorial by CM Hales (“Expanding the Treat-to-Target Toolbox for Obesity and Diabetes Care”) notes that “six deaths occurred in the two trials combined, all in the cagrilintide–semaglutide groups, including one suicide in each trial. Previous studies of suicidality with GLP-1 receptor agonist treatment have not supported a causal link,6 but it continues to be of concern.”
My take (from the editorial): “A sustainable treat-to-target approach should extend to lifelong maintenance of health gains after initial weight loss. The intensity and composition of lifestyle interventions in the context of highly effective pharmacologic therapies also need further study. The pharmaceutical pipeline is promising, with potential improvements in safety (such as preservation of lean mass) and more convenience for patients (such as oral administration and monthly dosing). Greater effects on the health of Americans may be achieved not with antiobesity medications producing ever greater magnitudes of weight loss but with expanded access to safe and effective therapies for those who would most benefit.”
Related blog posts:
