J Rutsky et al. JPGN 2024;79:622–630. Open Access! Predictors of celiac disease in patients with type 1 diabetes and positive tissue transglutaminase immunoglobulin A
This was a retrospective single-center study with 123 patients -60% had biopsy-proven celiac disease (CD).
Key findings:
- Higher titers were more likely to be associated with CD. The degree of TTG IgA elevation in patients with T1DM is correlated with the risk of CD; for every 10‐fold increase in TTG IgA, there is a 4.7× increased risk of celiac diagnosis.
- However, even with TTG IgA >10 x ULN, only 85% had CD.
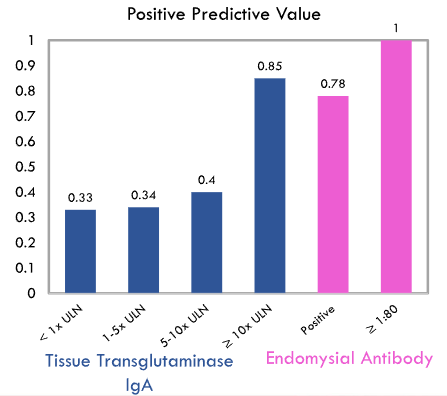
My take: Currently, the non-biopsy approach for CD diagnosis should not be used in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
Related blog posts:
- Celiac Disease: Pro Tips (Part 1)
- Why Celiac Serology Needs To Be Looked At Differently in Children with Type 1 Diabetes
- Celiac Diseaase and Diabetes
- Reappraisal of the Risk of Autoimmune Disease with Celiac, Plus One
- Celiac Disease: Pro Tips (Part 2)
- Celiac Disease: Pro Tips (Part 3)
- Celiac Disease: Pro Tips (Part 4)
- No-Biopsy Approach to Celiac Disease Diagnosis and Positive Predictive Value (Based on Population)
- ESPGHAN Guidelines for Diagnosing Coeliac Disease 2020

