- JP Weltzsch et al. Hepatology 2024; 80: 1026-1040. Optimizing thiopurine therapy in autoimmune hepatitis: A multicenter study on monitoring metabolite profiles and co-therapy with allopurinol
- Y Chung et al. Hepatology 2024; 80: 1000-1002. (Editorial) Open Access! Optimizing thiopurine therapy in autoimmune hepatitis: A multicenter study on monitoring metabolite profiles and co-therapy with allopurinol
Key findings:
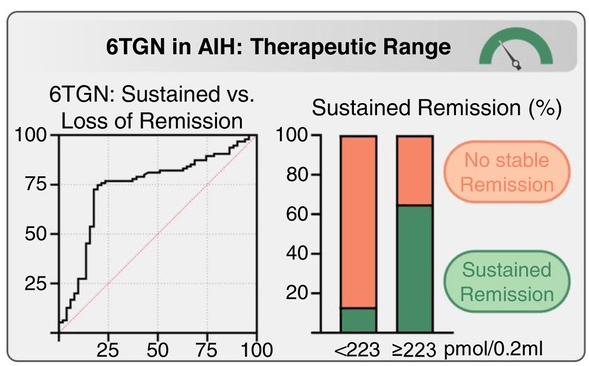
- Over 4 years (N = 146), patients with higher average 6TGN levels were associated with those with stable complete biochemical remission (CBR) (260 pmol/0.2 mL) compared to those failing to maintain CBR (181 pmol/0.2 mL; p = 0.0014) or never achieving CBR (153 pmol/0.2 mL; p < 0.0001), with an optimal 6TGN cutoff of ≥223 pmol/0.2 mL
- Adding allopurinol to thiopurines in difficult-to-treat patients (N = 36) raised 6TGN (168→321 pmol/0.2 mL; p < 0.0001) and lowered 6MMP (2125→184 pmol/0.2 mL; p < 0.0001), resulting in improved transaminases in all patients and long-term CBR in 75%.
- Limitation: most of the 337 patients did NOT have sequential azathioprine metabolite monitoring. This could indicate that the 146 patients with sequential monitoring could have a selection bias favoring patients with a more aggressive disease course. Thus, the proposed 6-TGN level of 223 may not be applicable for all patients.
From editorial:
- “In this issue of Hepatology, “Weltzsch et al1 conducted a multicenter study on the metabolic monitoring of thiopurines in AIH. The authors defined an optimal cutoff of ≥223 pmol/0.2 mL average 6TG level to maintain long-term biochemical remission (BR). Notably, 66% of patients with 6TG levels above this cutoff sustained BR rates.
- Allopurinol shifts the thiopurine metabolism toward 6TG production, allowing thiopurine dose reduction to 25%–30%, which improves efficacy and tolerability. (The 100 mg dose of allopurinol had more favorable 6MMP/6TG ratio).
- However, they note that in a prior study (J Hepatol 2021; 75: 324-32), “patients with subtherapeutic 6TG levels (75–225) achieved similar BR rates (75% vs. 81%, p = 0.589) to those with therapeutic levels (225–450), while experiencing significantly fewer adverse drug reactions (44% vs. 86%, p = 0.0002).”
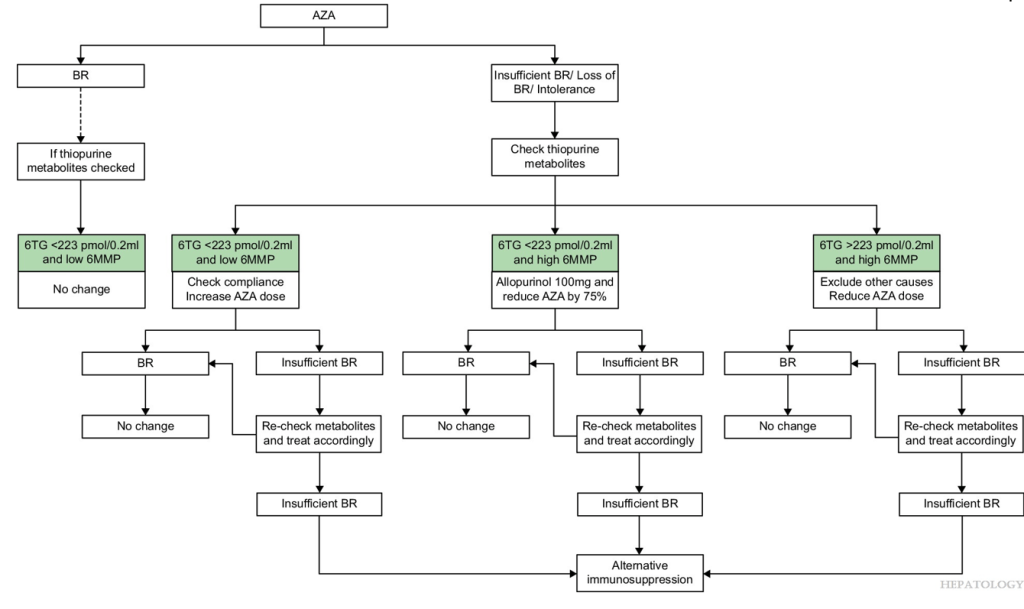
My take: This study shows in patients who have not achieved a biochemical remission, optimization of azathioprine dosing with metabolite monitoring improves biochemical remission. In those with low 6TG and low 6MMP, increasing the azathioprine should be considered. In those with low 6TG and high 6MMP, reducing azathioprine and adding allopurinol should be considered.
Related blog posts:
- Azathioprine metabolite measurement for Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Is First Line Therapy for Autoimmune Hepatitis Changing? CAMARO Study Results
- Diagnosing autoimmune hepatitis | gutsandgrowth
- Autoimmune Hepatitis, Horseshoes and Hand Grenades
- What to Do with Refractory Autoimmune Hepatitis: Case Report
- Is It a Mistake to Use Budesonide for Autoimmune Hepatitis?
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Safety of Low Dose Steroids and Utility of Aminotransferases
- Mortality Risk With Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Why It Is Hard to Stop Immunosuppression with Autoimmune Hepatitis and Lower Bone Density with Fatty Livers
- Predicting Outcomes in Childhood Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Autoimmune Hepatitis -Early Response Associated with Remission
Disclaimer: This blog, gutsandgrowth, assumes no responsibility for any use or operation of any method, product, instruction, concept or idea contained in the material herein or for any injury or damage to persons or property (whether products liability, negligence or otherwise) resulting from such use or operation. These blog posts are for educational purposes only. Specific dosing of medications (along with potential adverse effects) should be confirmed by prescribing physician. Because of rapid advances in the medical sciences, the gutsandgrowth blog cautions that independent verification should be made of diagnosis and drug dosages. The reader is solely responsible for the conduct of any suggested test or procedure. This content is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a condition.
