F Muller et al. NEJM 2025;393:1239-1241. CD19 CAR T-Cell Therapy in Multidrug-Resistant Ulcerative Colitis
This case study involved the use of “autologous chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells targeting CD19 in a 21-year-old woman with severe multidrug-resistant ulcerative colitis, who had declined colectomy. Previous treatments with prednisolone, mesalamine, infliximab, ustekinumab, ozanimod, filgotinib, vedolizumab, upadacitinib, and cyclosporine combined with mirikizumab had not induced clinical remission.”
“Clinical and biochemical remission occurred and were maintained over the 14-week follow-up period… without the use of concomitant therapy. Endoscopic, histologic, and ultrasonographic assessments showed signs of mucosal healing over time….These data suggest the possibility that CD19 CAR T-cell therapy can induce rapid drug-free remission in refractory ulcerative colitis, a disease that was previously thought to be largely B-cell–independent, given that rituximab treatment showed no efficacy..”
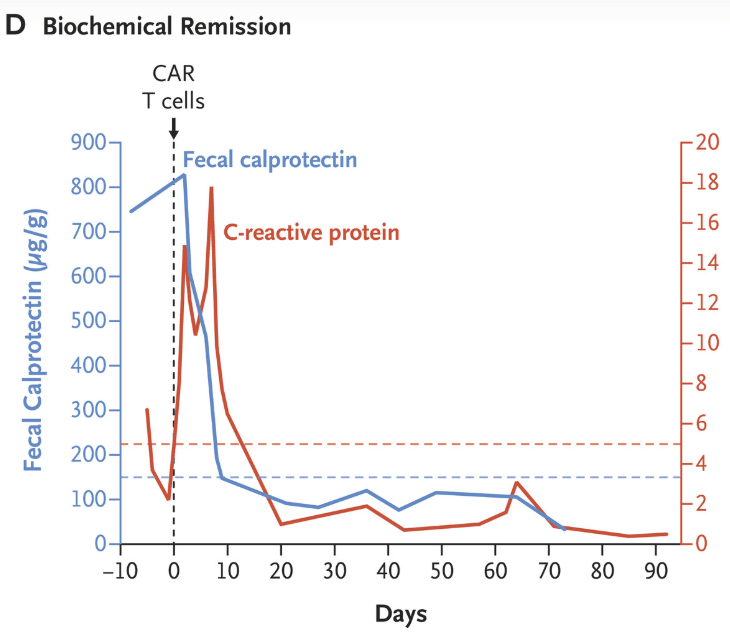
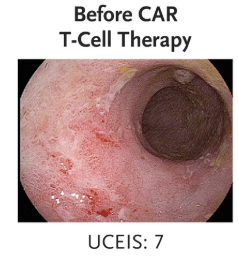
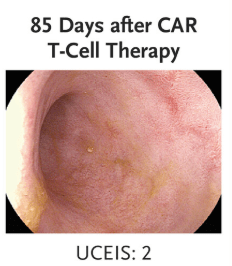
My take: This is only a single case report. However, it shows that modulation of the immune system could potentially cure ulcerative colitis. At the same time, long term adverse effects of CAR-T therapy will need to be monitored.
Related blog posts:
- From Treatment to Cures for Autoimmune Diseases
- CAR T-cell Therapy: A Cure for Autoimmune Disease?
- Great Story -How CAR-T Came About
