JEM O’Donnell, U Krishnan. JPGN 2022; 75: 556-563.Infectious Esophagitis in Children
Key points:
- Three most common causes of infectious esophagitis in children: Candida, HSV and CMV. Asperigillus (& other fungi) as well as bacterial esophagitis are rarely seen. Rare viral infections include human papilloma, varicella zoster and EBV
- For Candida, this is typically a benign commensal organism but can become pathogenic due to changes in immunity (immunocompromised including corticosteroids), altered motility and sometimes after antibiotics (with or without PPI therapy). EoE can present with similar-appearing mucosa; thus, biopsy and/or brushing is needed.
- With HSV, pediatric case series have reported higher rates in immunocompetent children
- Typical treatments: fluconazole for Candida, and Acyclovir for HSV. For CMV, potential treatments include ganciclovir, valganciclovir, foscarnet or cidofovir.
My take: This is a short, good review of the infections that can cause esophagitis in children.
Related blog post: Image Only: Candida Esophagitis
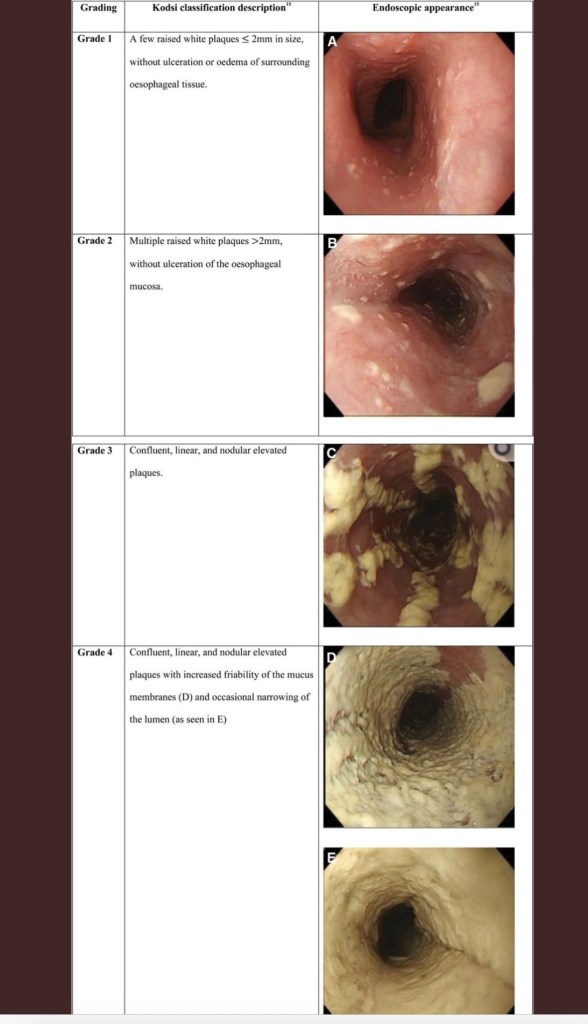
From JPGN twitter feed: Kodsi classification of esophageal candidiasis.

