Several recent articles have confirmed the benefits of H pylori eradication on reducing the risk of gastric cancer. This is in both Western and Eastern populations.
- A-K Wiklund et al. Gastroenterol 2025; 169: 244-250. Open Access! Risk of gastric adenocarcinoma after eradication of Helicobacter pylori.
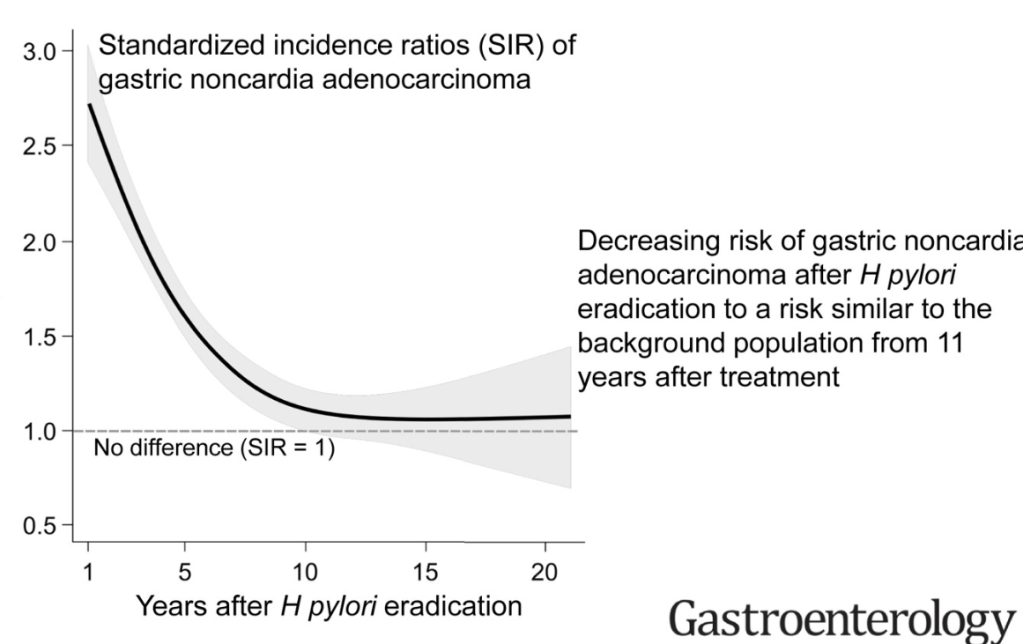
In this retrospective study from Nordic countries (Denmark, Sweden, Norway, Finland, and Iceland), researchers followed outcomes among ~700,000 people treated for H. pylori infection. The incidence of gastric adenocarcinoma was twice that of the general population in the first 5 years after treatment, likely reflecting H. pylori–related carcinogenesis that already was underway, but after 11 years, the incidence fell to that of the general population and remained there.
Discussion points:
- The results of this study from 5 entire Western countries are in line with systematic reviews from Asian populations, indicating that H pylori eradication reduces the risk of gastric cancer
- In addition, it has been proposed that eradication of H pylori might increase the risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma, but our recent study based on the NordHePEP found no such increase (Ref: Gastroenterology. 2024; 167:485-492.e3)
- Jung YS et al. Gastroenterol 2025; 169: 251-260. Preventive effect of Helicobacter pylori treatment on gastric cancer incidence and mortality: a Korean population study
In this population-based study with more than 900,000 individuals, gastric cancer incidence and mortality rates were significantly lower in H pylori-treated individuals than in the general population.
- Ford AC et al. Gastroenterol 2025;169:261-276. Open Access! Eradication therapy to prevent gastric cancer in Helicobacter pylori–positive individuals: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies.
In this meta-analysis of 11 randomized trials and 13 cohort studies researchers compared outcomes in treated and untreated H. pylori–positive adults. In both groups of studies, gastric cancer incidence was 40% lower in people who underwent H. pylori eradication. All but two of these studies were from eastern Asia.
- Z-C Liu et al. Gastroenterol 2025; 169: 205-207. Open Access Commentary! Revisiting Helicobacter pylori Eradication: Evolving Evidence and Global Implications for Gastric Cancer Prevention
“In 2025, the IARC Working Group has issued a new report reaffirming H pylori eradication as a globally actionable and cost-effective intervention for the primary prevention of GC.18…Also, addressing the global public health challenge of antibiotic resistance remains essential, necessitating the development of susceptibility-guided or empirically optimized regimens tailored to local resistance patterns.
My take (borrowed from the commentary): “Despite the challenges, collectively, the emerging evidence from diverse populations reinforces the significant benefits of H pylori eradication in reducing GC incidence and mortality. These findings continuously support that H pylori eradication remains an effective preventive strategy across demographic settings, highlighting its relevance as a critical public health measure globally.”
Related blog posts:
- Synergistic Dangers: Helicobacter Pylori and Cancer Genes
- Treating Helicobacter Pylori Lowers The Risk of Gastric Cancer
- Helicobacter Pylori: Relationship to Cancer and Dubious Beneficial Claims
- Dr. Benjamin Gold: 2024 Pediatric H pylori Guidelines (Part One)
- Dr. Benjamin Gold: 2024 Pediatric H pylori Guidelines (Part 2)
- Getting Rid of H pylori Does Not Increase the Risk of Esophageal Adenocarcinoma
- Give the Right Dose (for H pylori) -It Works Better!
- Long Term Benefits of Helicobacter Eradication in U.S.
