A Phillip et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025;81:913–921. A narrative review of the ileal pouch in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease and familial adenomatous polyposis
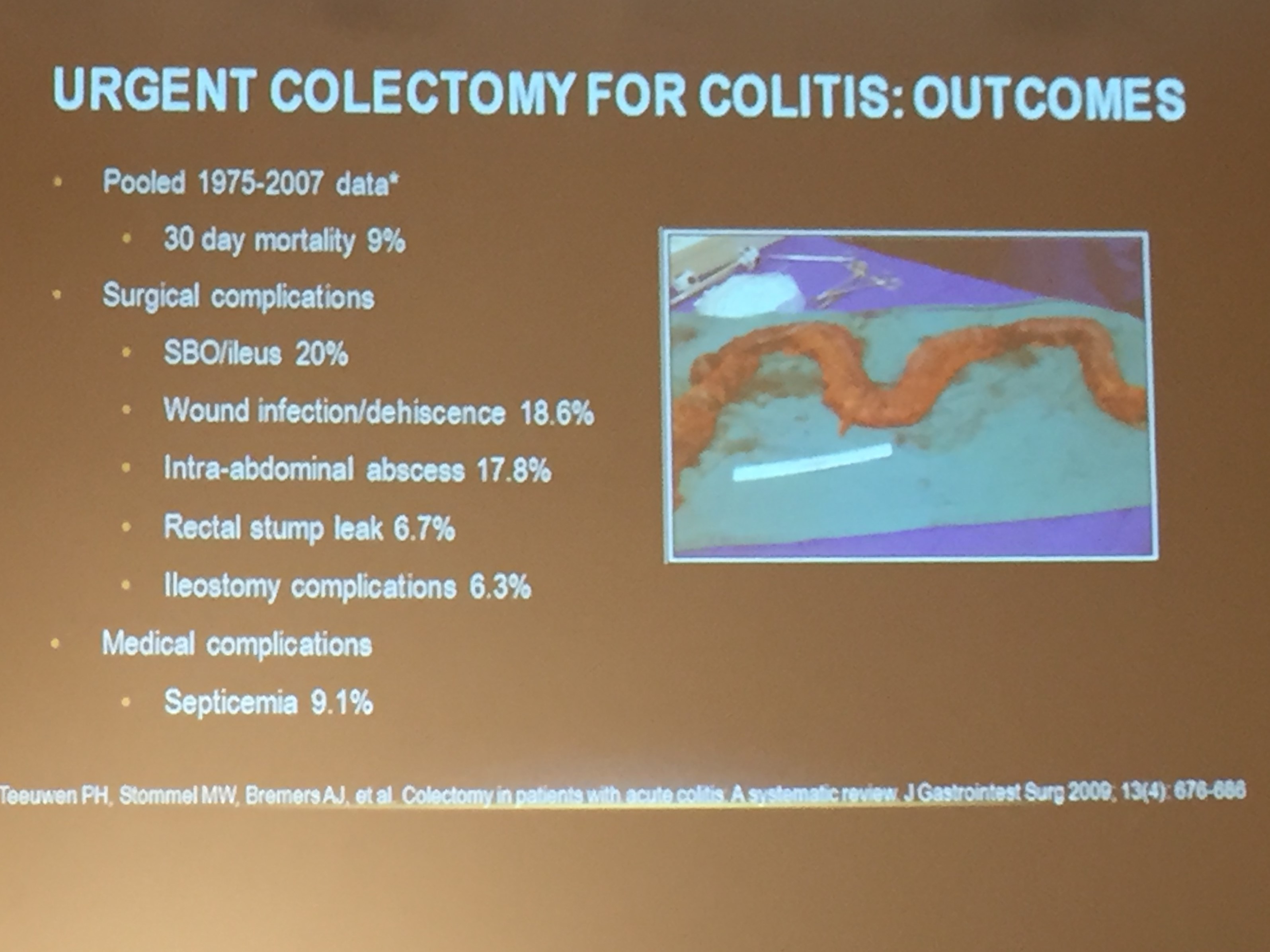
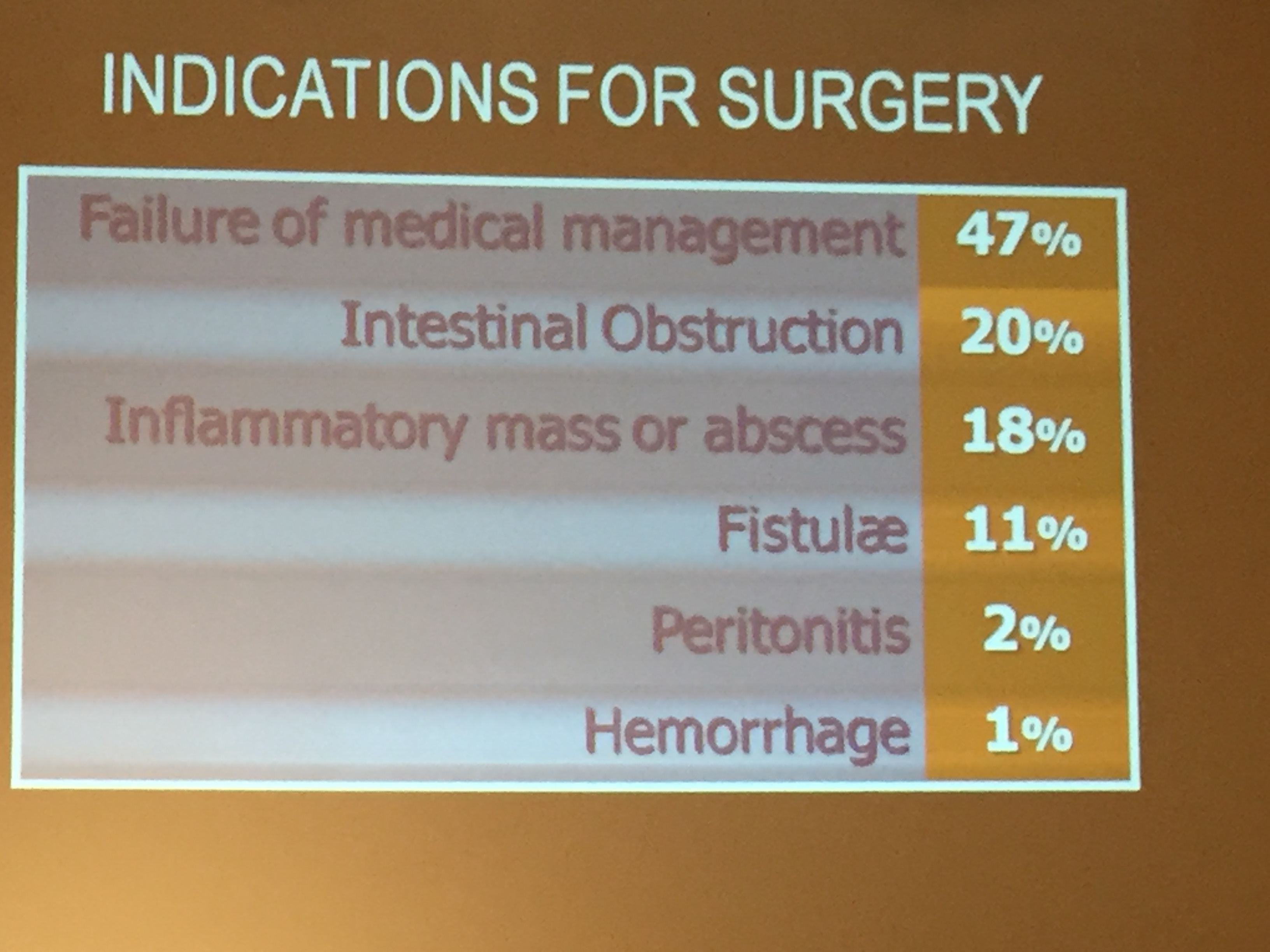
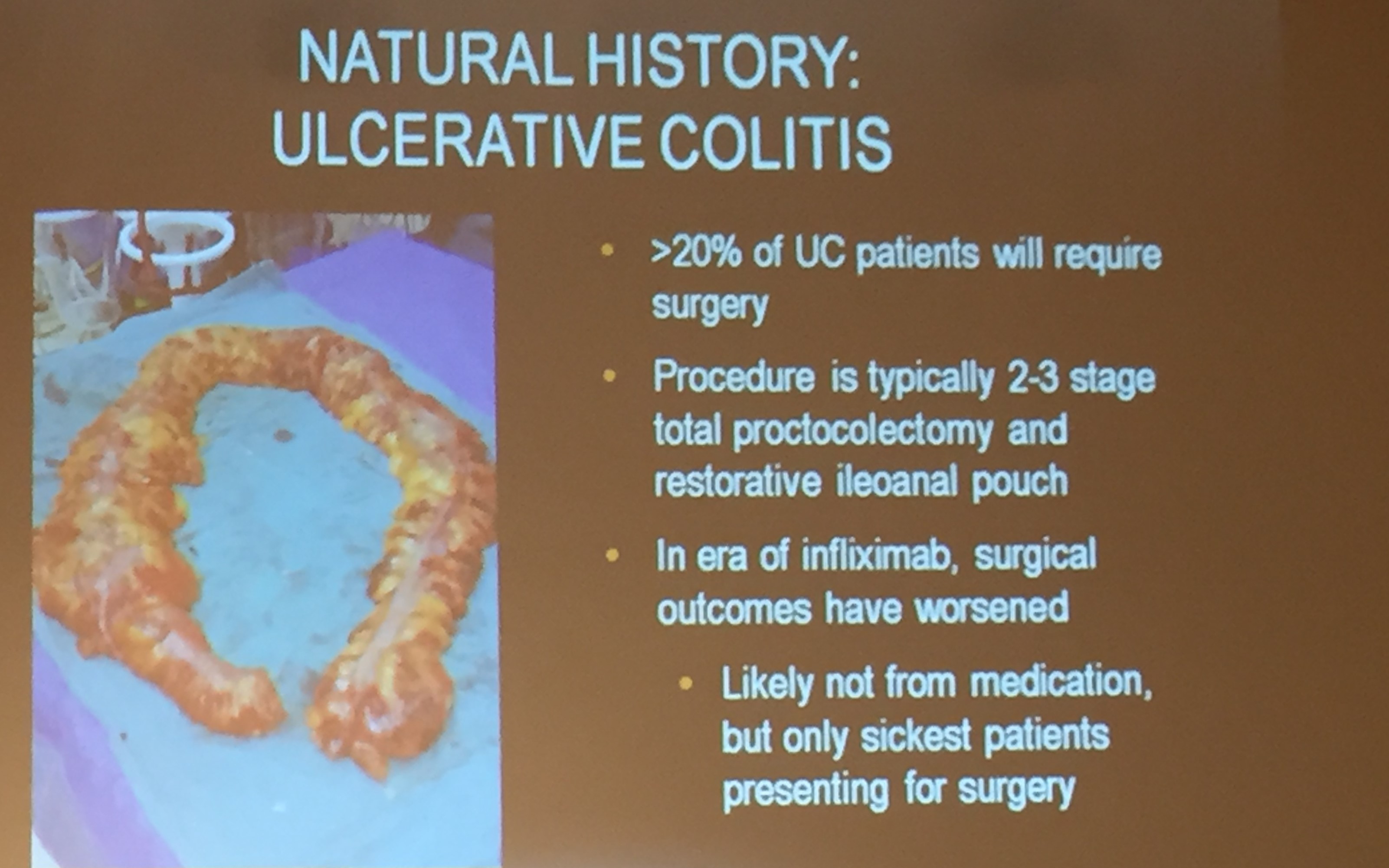
Introduction: Total proctocolectomy with ileal pouch-anal anastomosis (IPAA) can be a life changing solution for a subset of pediatric inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) patients. For patients with severe disease a three-stage approach is commonly performed.
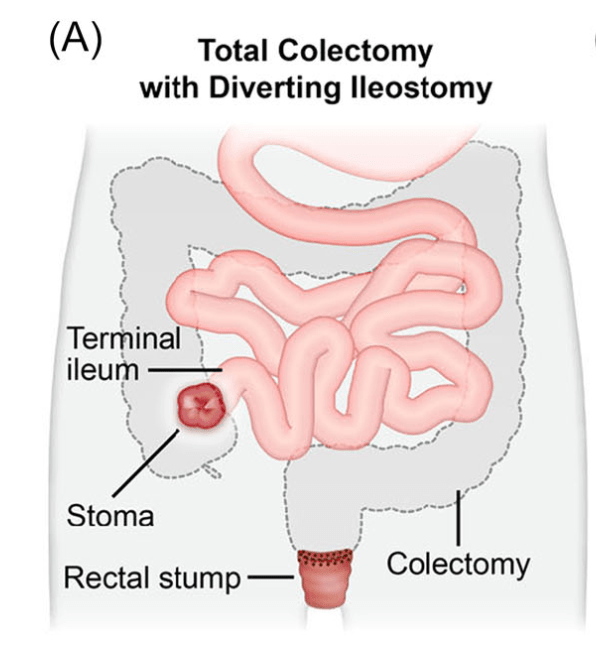
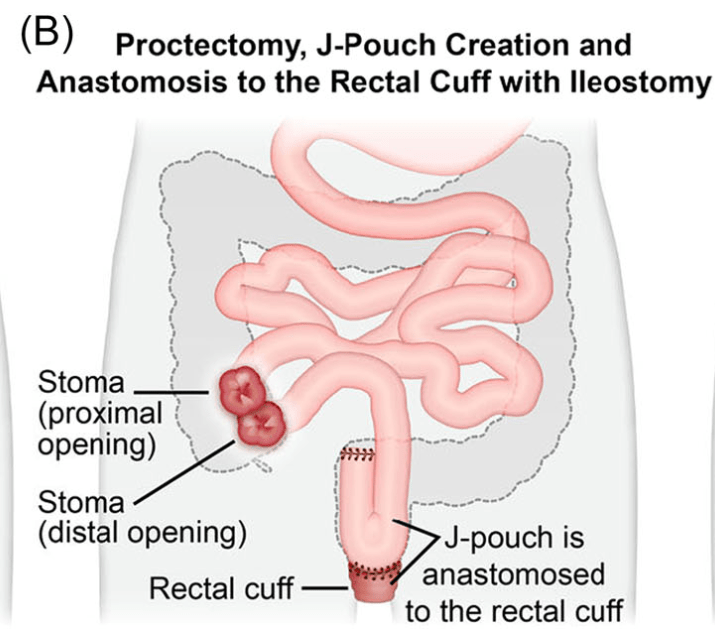
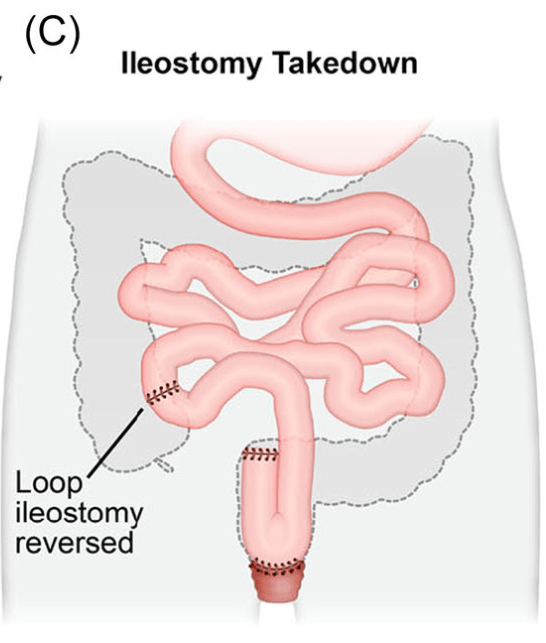
Creation of IPAA -Three Stages:
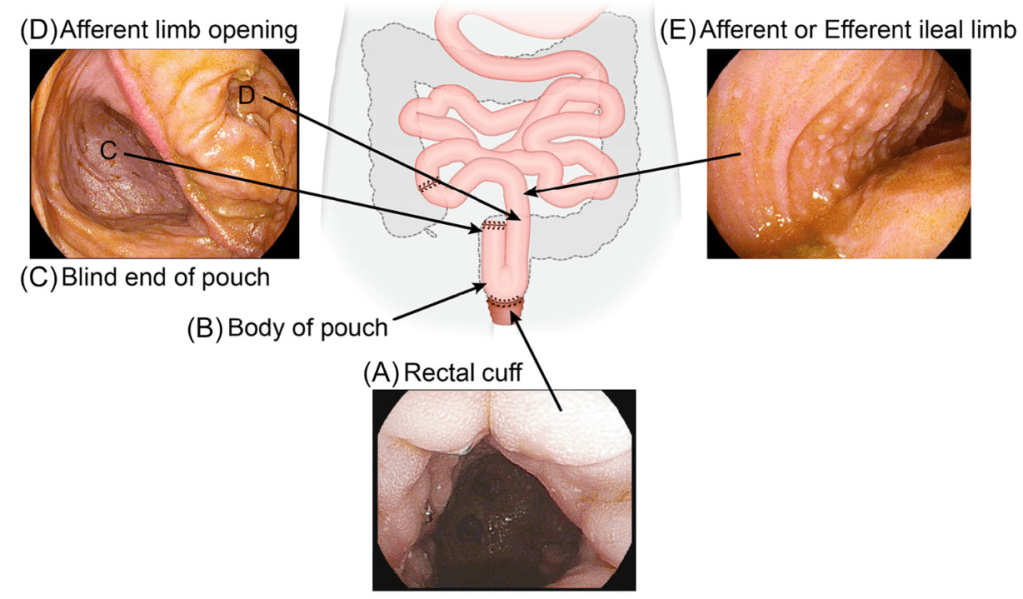
Endoscopic Images and IPAA Anatomy:
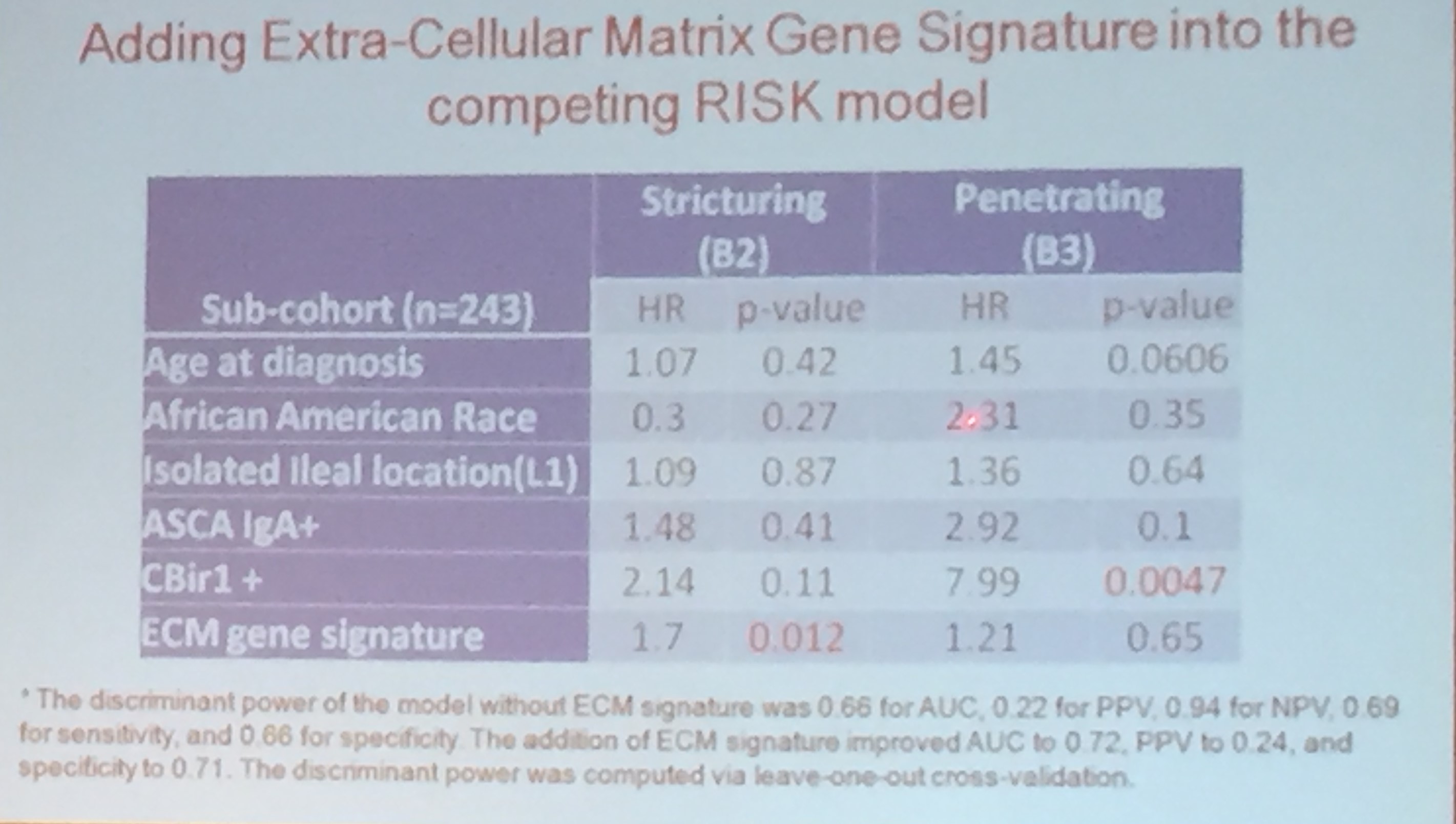
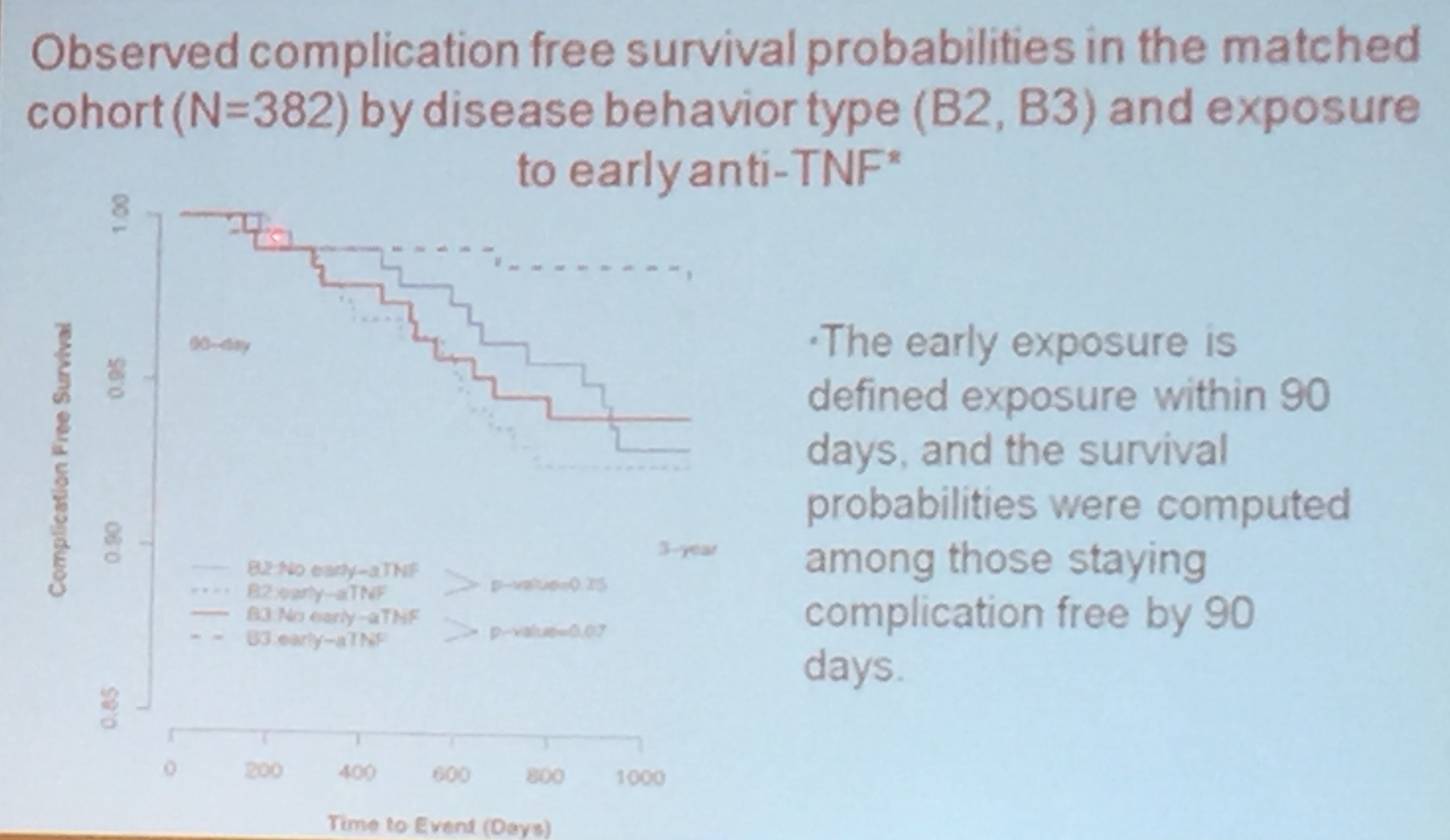
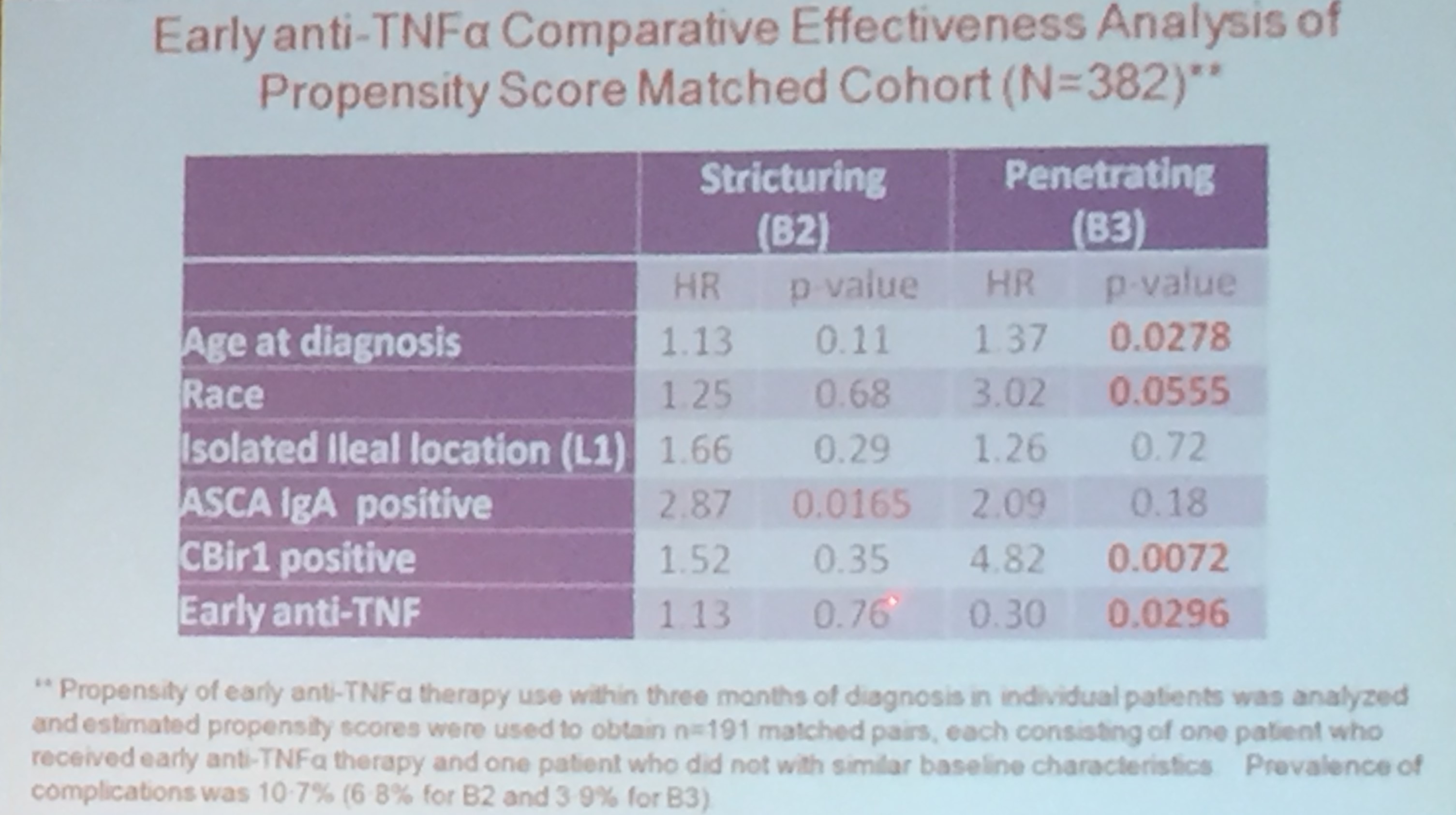
- The article provides guidance on complications including pouchitis, CD-like inflammation of the pouch, J-pouch failure, fertility after IPAA along with follow-up/screening recommendations.
- As for screening, adult guidelines recommend annual screening for IBD patients with high risk features—previous dysplasia, primary sclerosing cholangitis, type C mucosa, refractory pouchitis. In those without these features, guidelines are variable, with one suggesting screening every 5 years. In FAP patients, the recommendation for surveillance screening following IPAA is pouchoscopy every 1–2 years.8
My take: Most pediatric gastroenterologists are not proficient in pouch management due to the small number of our patients needing IPAA. This review provides a terrific review/resource.
Related blog posts:
- AGA Guideline on Pouchitis Management (2024)
- Endoscopy of the Ileal Pouch Anal Anastomosis
- Chicago Classification of J Pouch Outcomes
- The Importance of the EARNEST Trial –Vedolizumab for Chronic Pouchitis
- What is Going On With Pouchitis? & No More Handshakes
- Vedolizumab for Chronic Pouchitis
- IPAA (Pouch) for Crohn’s Disease and Indeterminate Colitis