- NPR (Jan 30, 2023: Wegovy works. But here’s what happens if you can’t afford to keep taking the drug A study found that most people gain back most of the weight within a year of stopping the medicine…The rebound weight gain is not a surprise given how the medication works. Wegovy’s active ingredient — semaglutide — is a GLP-1, or glucagon-like peptide-1, which mimics the GLP-1 satiety hormone in our bodies. When we eat, GLP-1 is released from our intestines and sends signals to our brain centers that control appetite.
- JPH Wilding et al. Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism 2022. https://doi.org/10.1111/dom.14725 Open access! Weight regain and cardiometabolic effects after withdrawal of semaglutide: The STEP 1 trial extension “One year after withdrawal of once-weekly subcutaneous semaglutide 2.4 mg and lifestyle intervention, participants regained two-thirds of their prior weight loss, with similar changes in cardiometabolic variables. Findings confirm the chronicity of obesity and suggest ongoing treatment is required to maintain improvements in weight and health.”
- J Belluz. NY Times Jan 31, 2023: What New Weight Loss Drugs Teach Us About Fat and Free Will
This article discusses several conditions like Prader-Willi and pregnancy that can result in increase hunger and then elaborates on genetic tendency towards obesity in an age of abundant ultra-processed high calorie foods. Excerpts:
A famous 1990 study of identical twins born in Sweden showed that pairs who were separated at birth and adopted had weights more similar to each other than to their adoptive families…The ability to sense such fullness — and hunger — varies, the result of genetic differences in brain circuits that control appetite.
The new drugs are the first to manipulate the hormonal regulatory systems governing energy balance. The drugs simulate the action of our native GLP-1 but with longer-lasting effects, amplifying the fullness signal inside the body…At the very least, though, the way the drugs work can teach us that people who are larger did not necessarily choose to be, just as people who are smaller did not — and are not morally superior. This “isn’t a free pass, either to individuals who do have the capacity to choose better, nor does it take the heat off of food industries,” said a University of Sydney nutritional biologist, Stephen Simpson, but it’s “evidence that obesity isn’t a personal lifestyle choice.”
My take: For those who benefit from GLP-1 medications, it is important to recognize that weight gain is likely when the medications are discontinued; this indicates once treatment is started, the goal would be to use indefinitely –until something better comes along.
Related blog posts:
- What Really Causes Obesity and Weight Bias
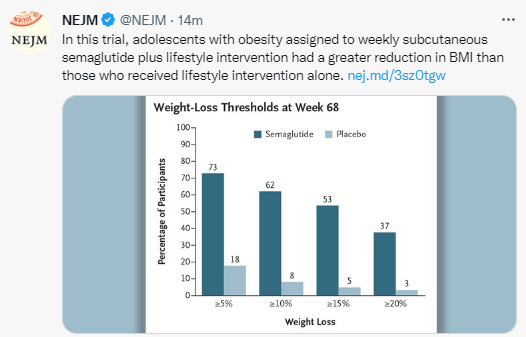
- Semaglutide in Adolescent Obesity
- AGA Guidelines for Adults with Obesity
- Does Motivational Interviewing Help Long-Term Outcomes for Obesity?
- Time to Change the Medical Treatment and Attitudes Directed at Obesity?
- How to Talk About Childhood Obesity

Disclaimer: This blog, gutsandgrowth, assumes no responsibility for any use or operation of any method, product, instruction, concept or idea contained in the material herein or for any injury or damage to persons or property (whether products liability, negligence or otherwise) resulting from such use or operation. These blog posts are for educational purposes only. Specific dosing of medications (along with potential adverse effects) should be confirmed by prescribing physician. Because of rapid advances in the medical sciences, the gutsandgrowth blog cautions that independent verification should be made of diagnosis and drug dosages. The reader is solely responsible for the conduct of any suggested test or procedure. This content is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a condition