This blog entry has abbreviated/summarized this terrific presentation; most of the material has been covered in this blog in prior entries but still this was a useful review. Though not intentional, some important material is likely to have been omitted; in addition, transcription errors are possible as well.
2nd Lecture: What is Next in Treatments for Pediatric Patients? –Dr. Michael Rosen
I really enjoyed meeting Dr. Rosen. He is super-friendly and knowledgeable.
Combination therapy. Grossi V et al showed improvement in infliximab durability with concomitant therapy.
Now starting COMBINE trial (ImproveCareNow)–randomized to low dose MTX or placebo in combination with anti-TNF agent.
Therapeutic drug monitoring in pediatrics. Is this an alternative to combination therapy? Rationale (see slide): lower antibody formation if trough levels maintained. IFX level >5.5 associated with persistent remission (Singh et al 2014). Children are growing and they may need more adjustments. In Cincy, checking levels at week 14 after initiation and then every 6-12 months.
Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis. High rates of dose escalation in this population. Some of this is due to more rapid clearance of anti-TNF –leaking in gut and other mechanisms as well. Week 8 level of 40 associated with clinical response. Thus, this population may benefit from 10 mg/kg at start (in those with albumin <3) and may need more frequent dosing, especially early into treatment (?0, 2, 6, 10). ARCH study to look into this further
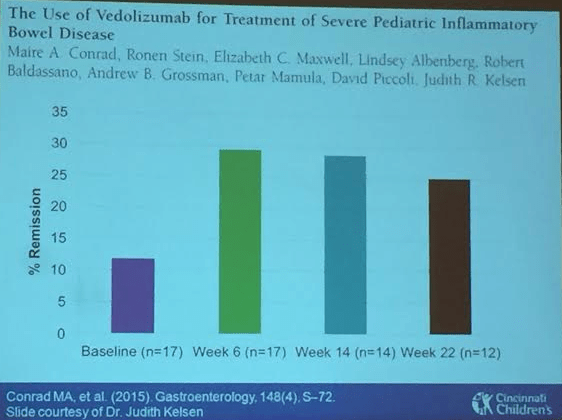
Vedolizumab. Conrad MA 2015. About 1/3rd of these refractory patients in this abstract responded.
Ustekinumab . IL-12 & IL-23 blockage. No studies in pediatrics. Case report reviewed of good response in a refractory case.
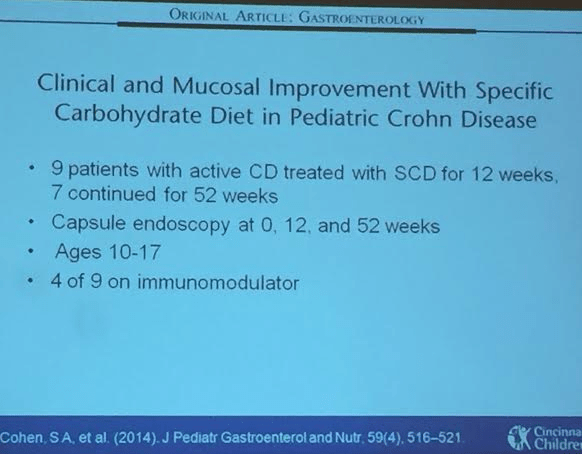
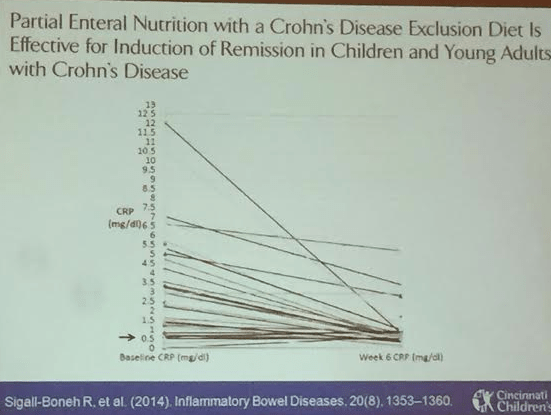
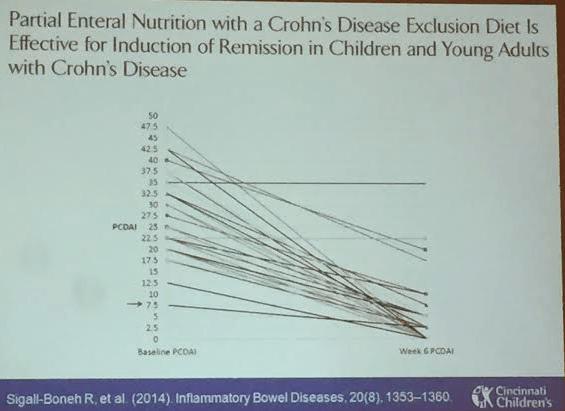
Enteral therapy. Specific carbohydrate diet experience. These diets have some published data, most retrospective studies. Our group (Cohen SA et al) did perform a small prospective study. Sigall-Boneh R et al showed improvement with partial enteral nutrition.
Very early-onset of IBD. IL-10 receptor deficiency was a key early discovery and can be treated with stem cell transplant. STAT3 mutation case reviewed which was managed with tocilizumab. More targeted therapy expected based on specific mutations.