AJ Gumm, EB Rand. J Pediatr 2025; 277: 114389. Fontan-Associated Liver Disease
This review article provides a lot of useful advice regarding Fontan-Associated Liver Disease (FALD).
Key points:
- FALD prevalence: “will be 70,000 by 2025, with the mean age of 23 years”
- Early common manifestations are modest increases in AST and ALT. Elevation of bilirubin is a late finding. Mild elevation of INR is common in range of 1.4 to 1.8.
- Ascites occurs in 2-17% of patients with FALD but can be due to other etiologies like PLE
- Annual labs (HFP, GGT, CBC/d, PT/INR, AFP) recommended after 7 years post-Fontan
- No special diet is recommended but it is worthwhile to avoid fatty liver disease
- For varices, a TIPS procedure “may precipitate pulmonary hypertension resulting in cardiac failure.” ‘The safety of a nonselective beta-blocker to prevent a variceal bleed has not been established.” It is important to determine if there are cardiac options that could improve portal hypertension.
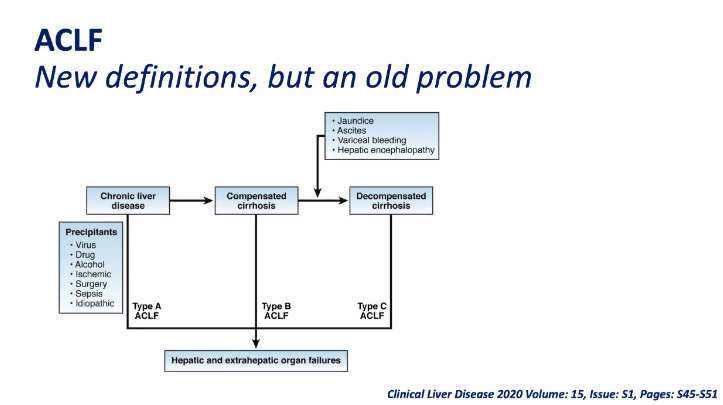
- In patients with advanced liver disease, multidisciplinary teams are needed to determine if an isolated liver transplantation versus combined heart and liver transplantation (CHLT) is needed.
- “If a patient requires a heart transplant, the presence of liver fibrosis or even cirrhosis alone is not an indication for liver transplantation, because cirrhosis has been reported to reverse after isolated heart transplantation in a single provocative case. However, if there is evidence of cirrhosis and liver decompensation, then a CHLT should be considered.”
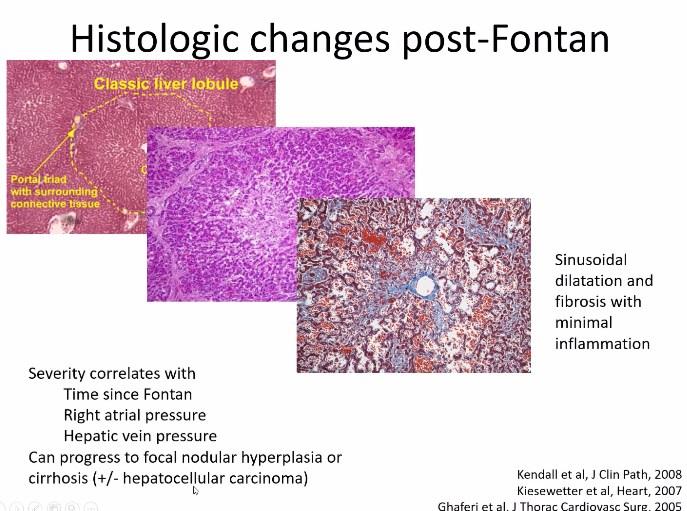
- Many hepatologists recommend trending elastography. Many recommend liver biopsy starting after 10 years status post Fontan
When to refer to hepatology:
- Concerning labs: high transaminases, GGT or bilirubin; low albumin (if liver-related), high INR (not due to warfarin), and high AFP
- Signs of portal hypertension (eg. splenomegaly, varies, reversal of flow on ultrasound)
- Liver masses
- More than 10 years post-Fontan. “100% of patients with Fontan circulation will develop liver disease in their lifetime”
My take: There is a lot that we do not know about FALD and management is complex due to coexistent abnormal cardiac physiology.

Related blog posts:
- Online Aspen Webinar (Part 9) -Liver Disease After Fontan, Acute on Chronic Liver Disease and Immunosuppression Withdrawal Strategies
- Success of Isolated Heart Transplantation in the Setting of Fontan-Associated Liver Disease & How COVID Vaccines Work
- More Cases of Hepatocellular Carcinoma after Fontan