Here’s a link to the new 10-page guidelines: Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Here are critiques:
- From NY Times:, Emily Oster 1/8/26: Kennedy Is Telling Americans How to Eat. It’s Not Crazy Advice and Roni Rabin 1/7/26 New Dietary Guidelines Abandon Longstanding Advice on Alcohol
- From AJC, Ronnie Robbins 1/11/26: Diet advisers weigh in on America’s new ‘real food’ approach
- From NY Times, Alice Callahan, Maggie Astor 1/09/26: Several of Kennedy’s Dietary Advisers Have Ties to Meat and Dairy Interests
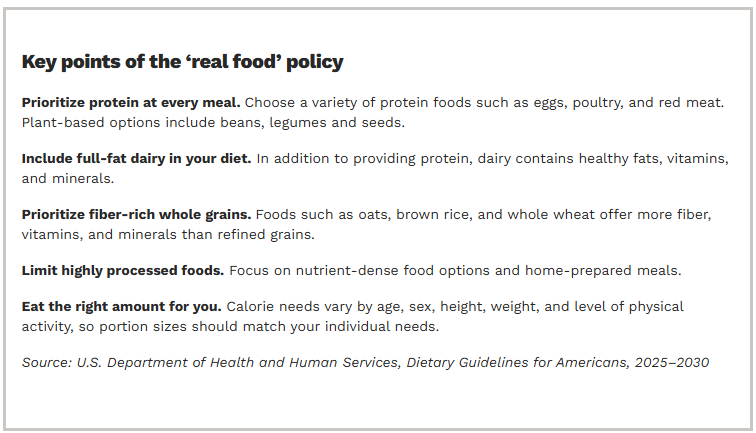
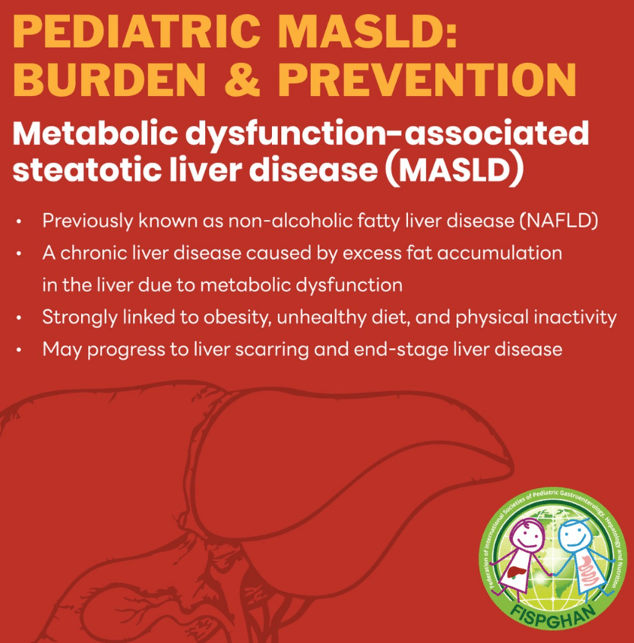
What’s Good About This Guidance:
- Short enough to read and understand
- The emphasis of reducing unprocessed foods and clear language
- Encouraging early introduction of potential allergens at 6 months of life. This lowers the risk of developing food allergies later.
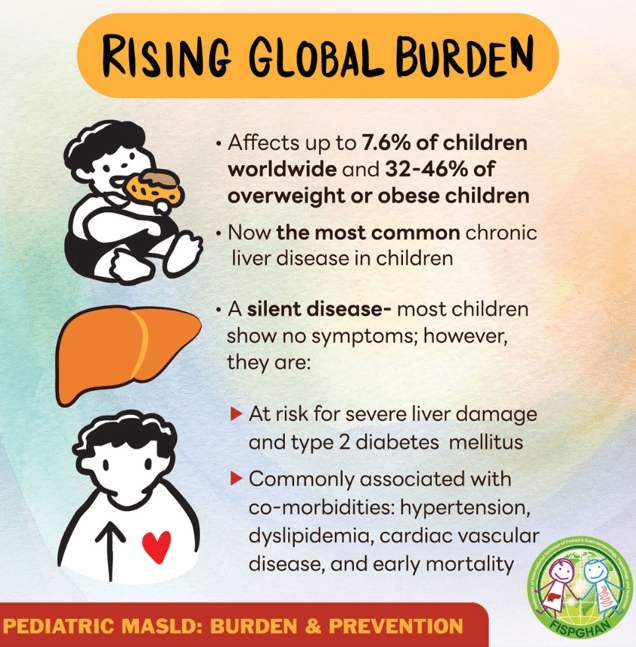
Some of the questionable advice:
- Increasing the protein recommendation to 1.2-1.6 gm per day, up to double prior recommendations. The reason why this level of protein is not a good idea for everyone is noted in a prior blog post: Is a High Protein Diet Beneficial and Safe?. And from the AJC critique: “Pushing protein higher can also crowd out vegetables and fiber, which play a major role in heart health, digestion and overall wellness.”
- Backing away from previous advice about alcohol. The current guidance states to “consume less alcohol.” From NY Times: “It is the first time in decades that the government has omitted the daily caps on drinking that define moderate consumption. The guidelines no longer warn of risks like cancer.”
- Encouraged changes (more red meat, full-fat dairy) may increase saturated fat intake above stated goal of less than 10%.
The NY Times article on conflicts of interests notes that “Robert F. Kennedy Jr. had promised that his panel, which released new guidelines this week, would have no “conflicts of interest”….Some parts of the guidelines represent such a departure from previous versions that it seems like the administration “handpicked” scientists likely to support those conclusions, “versus undertaking a neutral review of the science,” said Lindsey Smith Taillie, a professor of nutrition at the U.N.C. Gillings School of Global Public Health.”
My take: Overall, the focus on reducing processed foods and decreasing added sugar are worthwhile. The brevity of the guidelines make them accessible. At the same time, the guidelines appear to continue a pattern of RFK Jr of selecting advisers, whether with diet recommendations or with vaccine policy, to support a desired outcome.
Related blog posts:
- “Optimal dietary patterns for healthy aging”
- “How to Make America Healthy: the Real Problems — and Best Fixes”
- “You Can’t Outrun a Bad Diet”
- NY Times: “Our Food is Killing Too Many of Us”
- How Putting America First is Undermining Health Outcomes Here and Globally
- Impact of Ultra-Processed Foods on Bowel Health
- The Paramount Health Challenge for Humans in the 21st Century
- Call For Action: Adolescent Nutrition Series | gutsandgrowth
- Ultraprocessed Food and the Risk of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Is Red Meat More Likely to Cause High Cholesterol Than White Meat?
- For Increased Longevity: More Greens are Good
- Heart-healthy Mediterranean Diet
- Why Fiber (Fruits and Veggies) is Good for You
- Fresh Fruit Study
- Does a Healthy Lifestyle Result in Better Outcomes?
- It’s Complicated: The Relationship Between Milk and Health