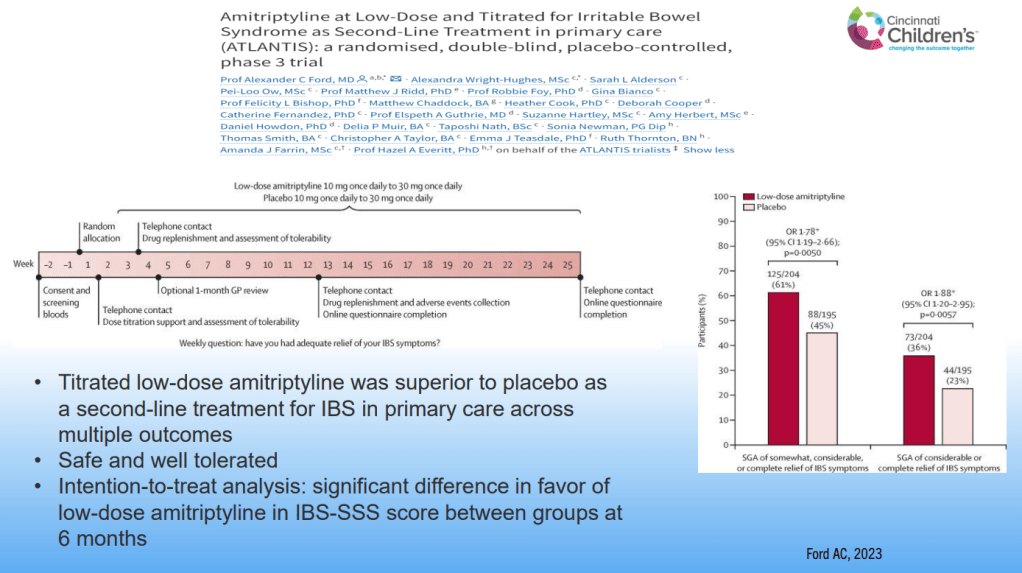
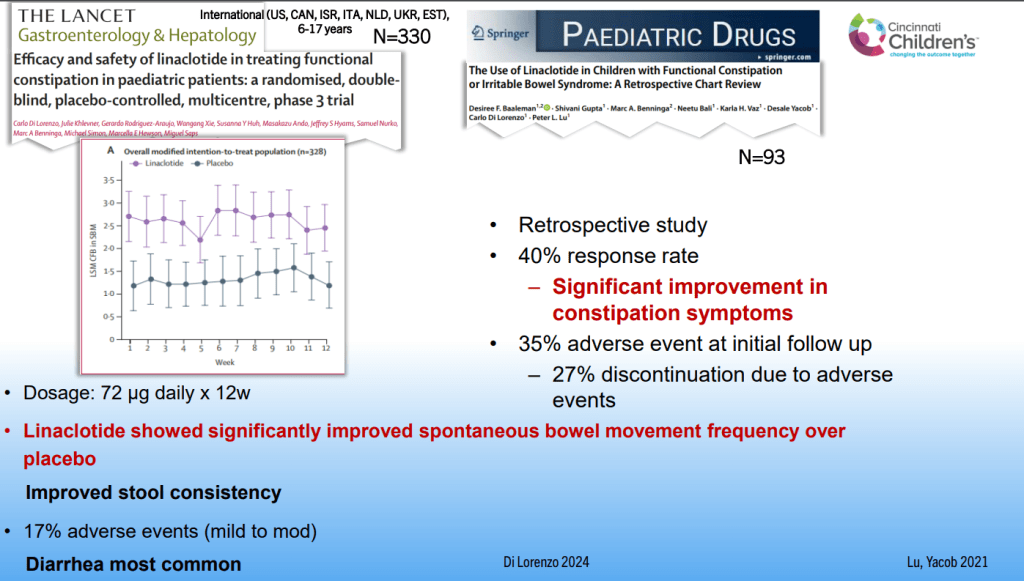
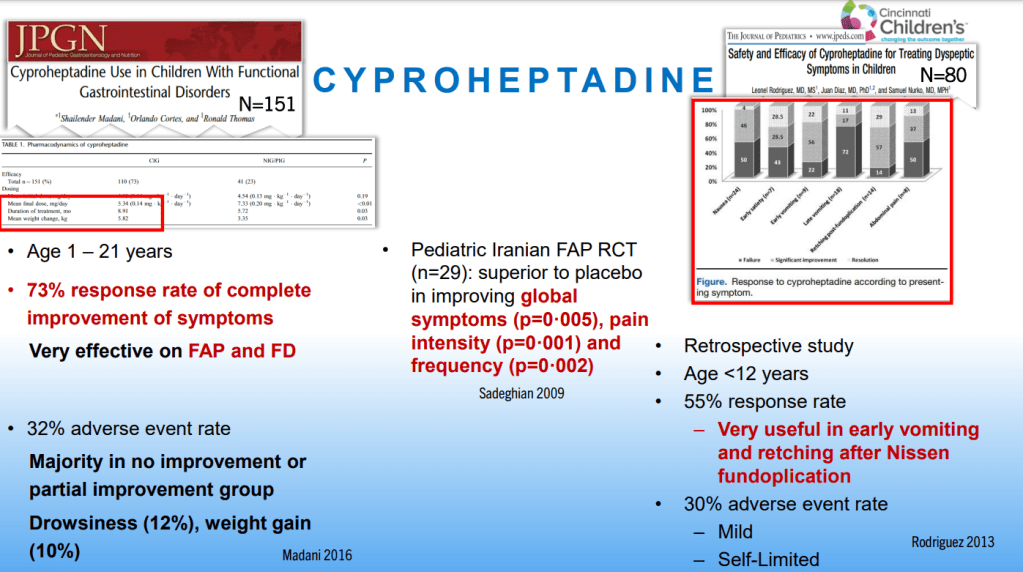
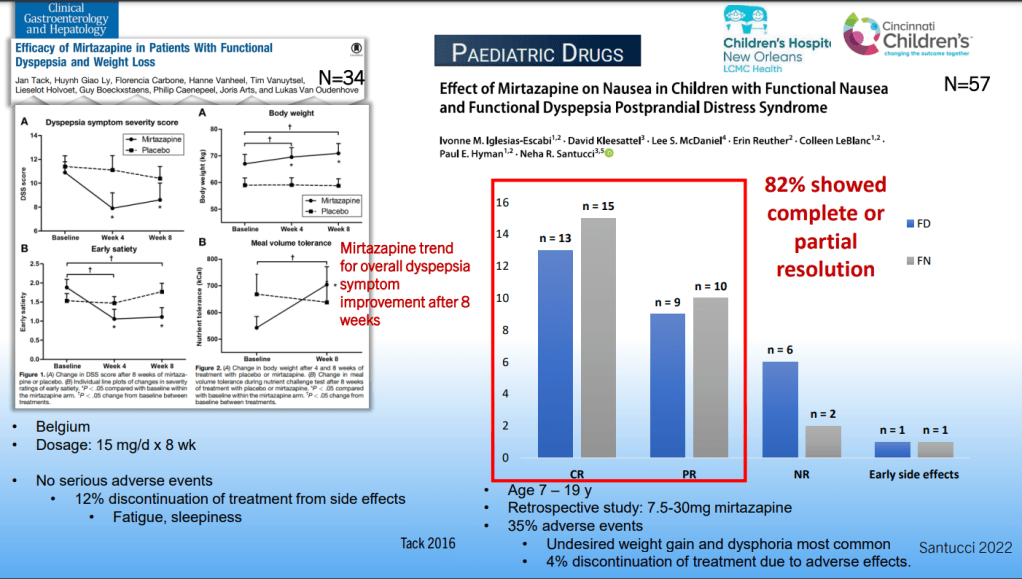
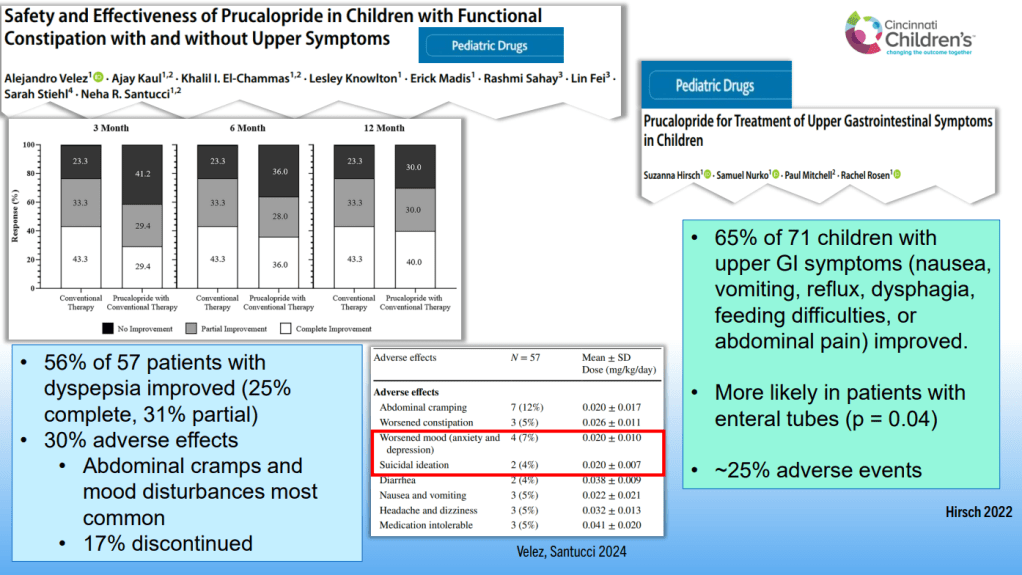
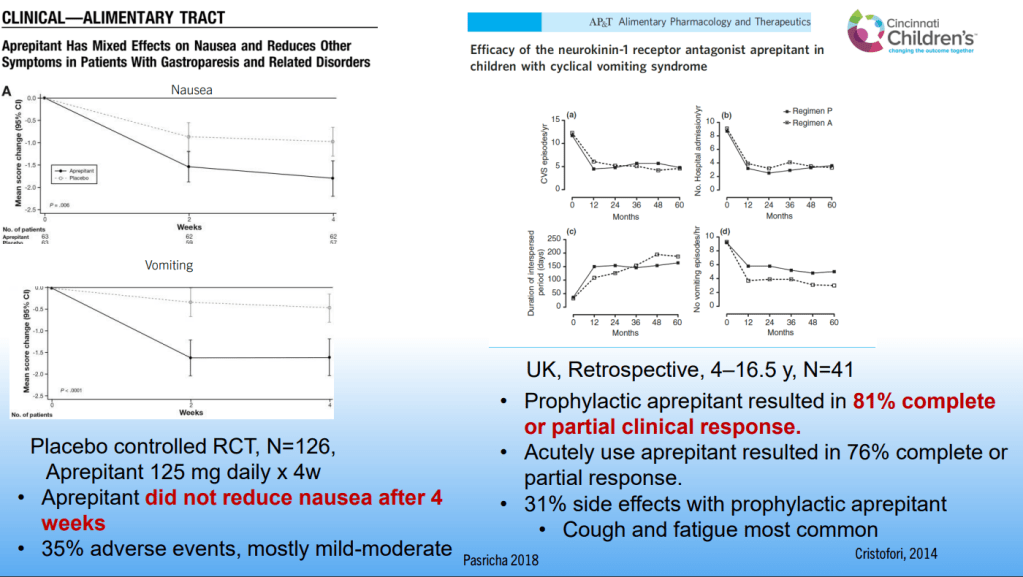
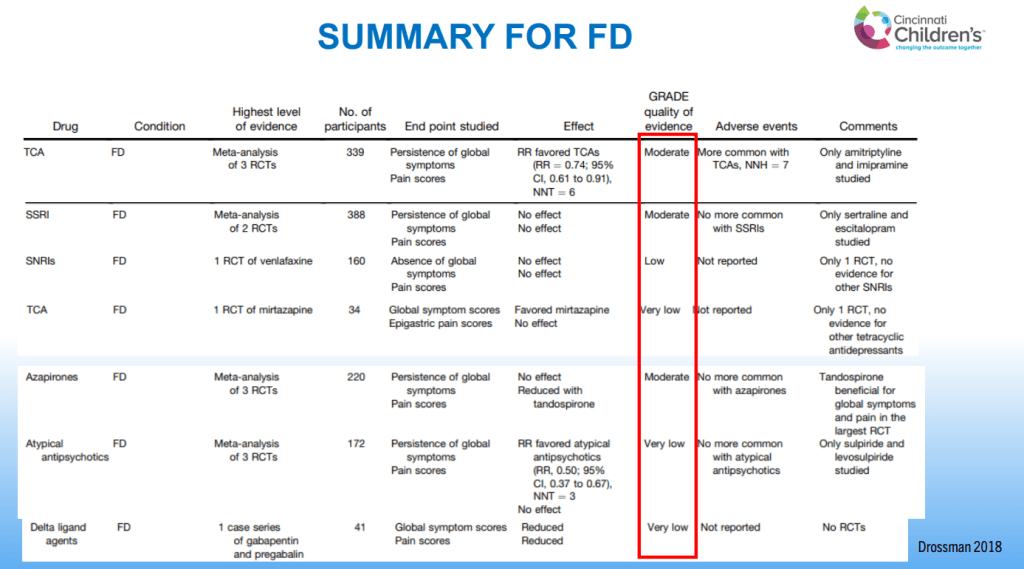
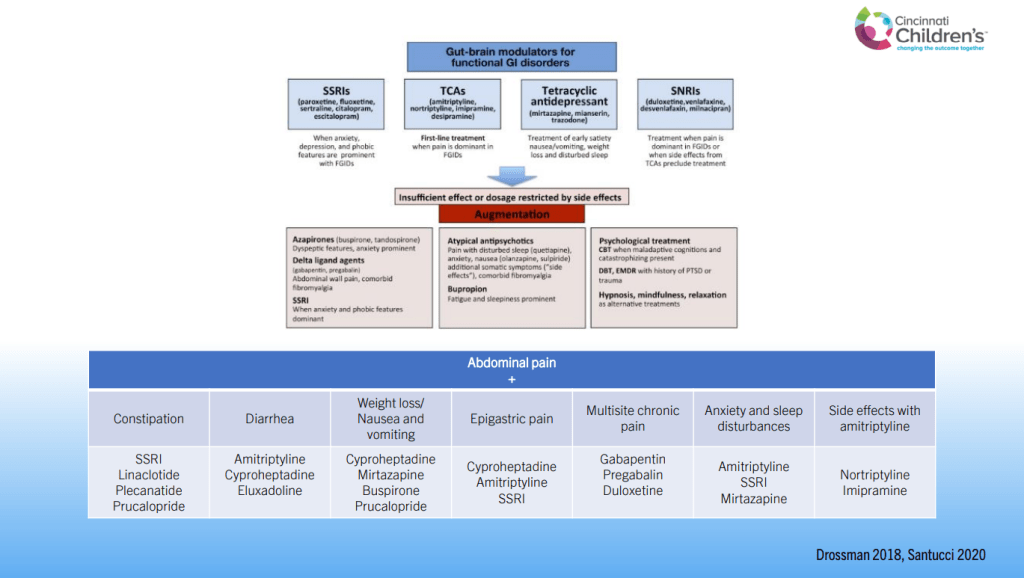
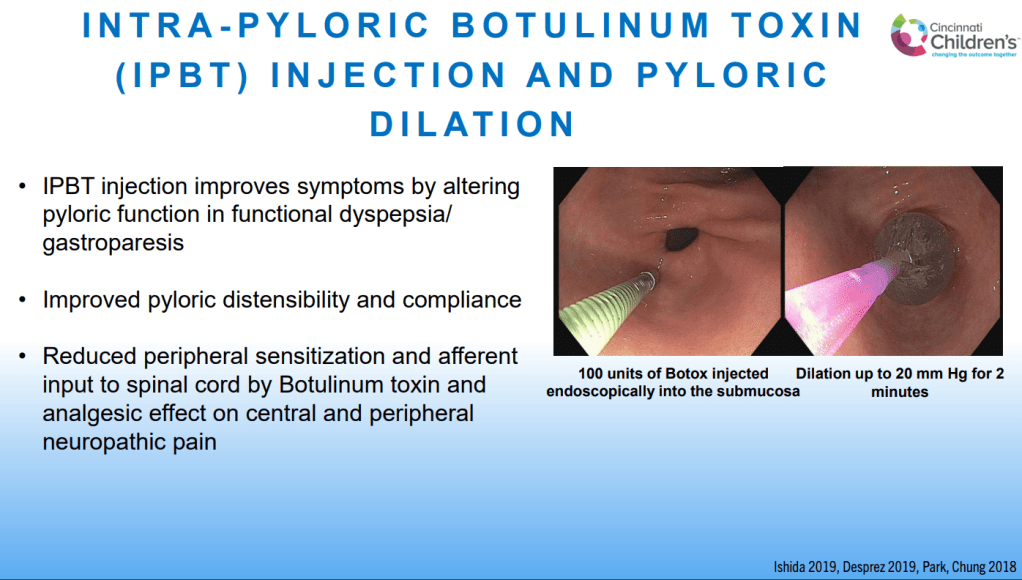
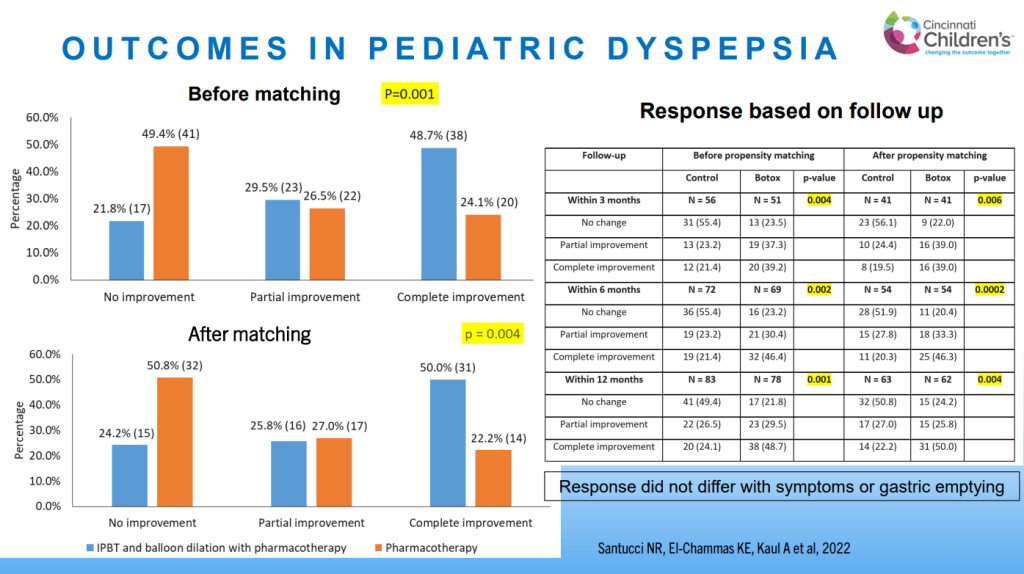
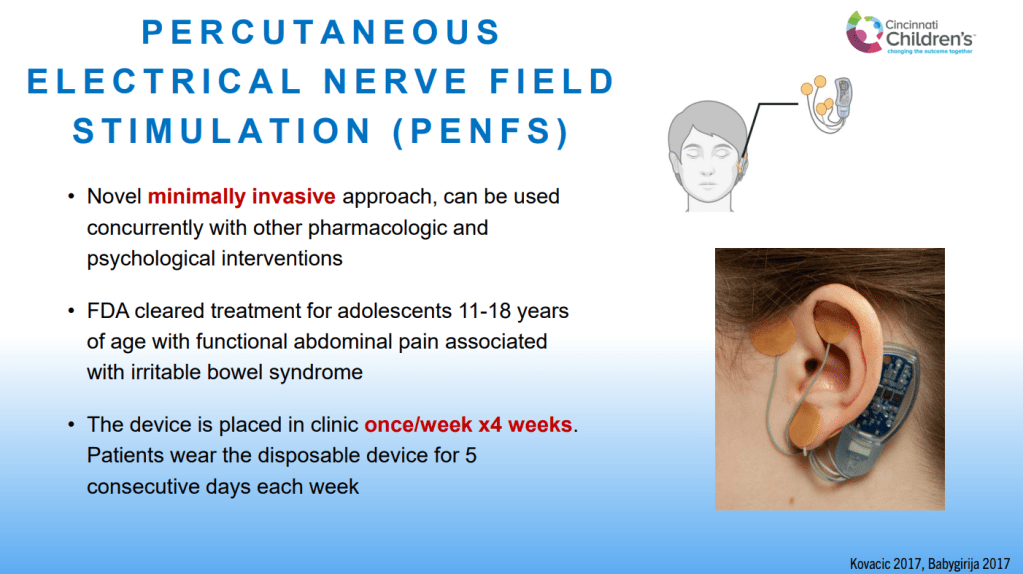
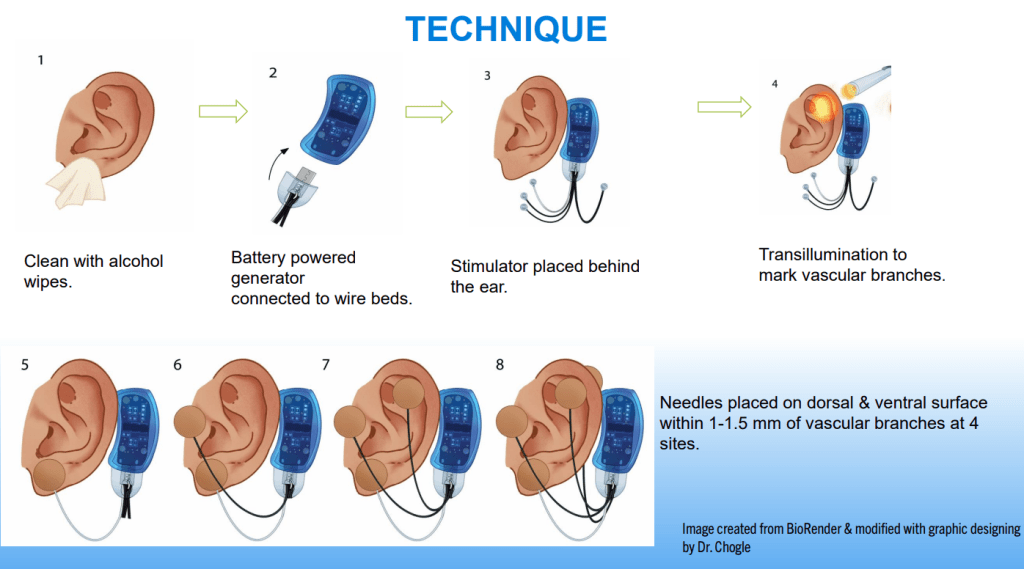
Dr. B Li, emeritus professor of Pediatrics (Medical College of Wisconsin), gave this year’s Billy Meyers Lecture. Dr. Li is considered the world’s foremost authority on cyclic vomiting syndrome (CVS) (‘the emperor of emesis’). He gave a fantastic update. I have taken some notes and shared many of his slides. There may be inadvertent omissions and mistakes in my notes. More information on the CVS 2025 guidelines is noted in a separate post: 2025 Pediatric Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome Guidelines


- Historical background of CVS: Early descriptions of CVS date back to 1880s and Samuel Gee (who also is credited with the first modern description of celiac disease). Charles Darwin was likely affected by CVS

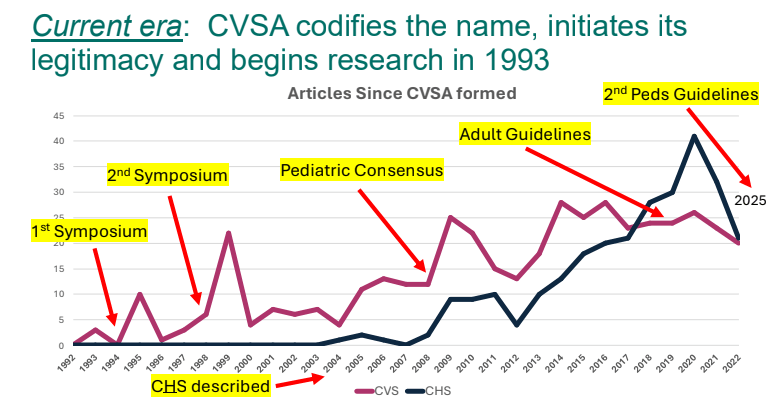
- Epidemiology: CVS is not a rare disorder. It likely affects ~2% of kids and adults
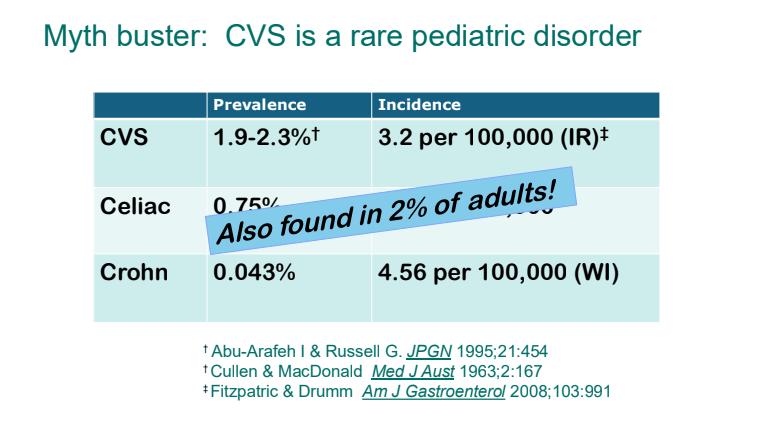
- There are several patterns of CVS. Many patients who have CVS do not have a cyclical pattern
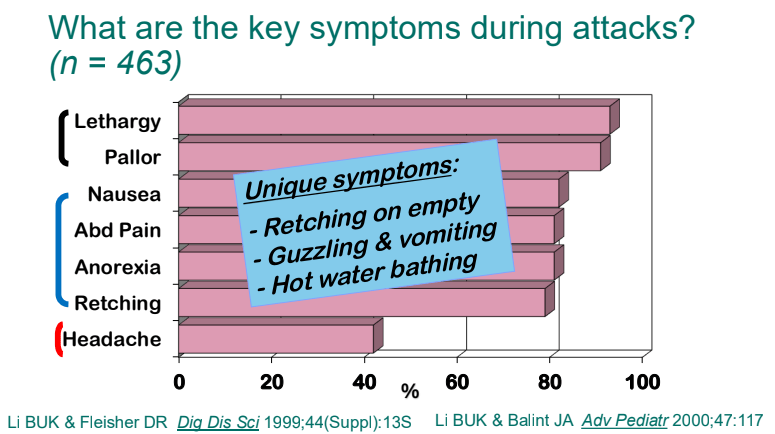
- Lethargy and pallor are common symptoms which make patients appear more ill
- Retching on an empty stomach and severe emesis are hallmarks and likely indicate that the primary mechanism is not due to the GI tract. Though there are some food poisonings (eg. Bacillus cereus) that can have some of these symptoms but typically milder in severity
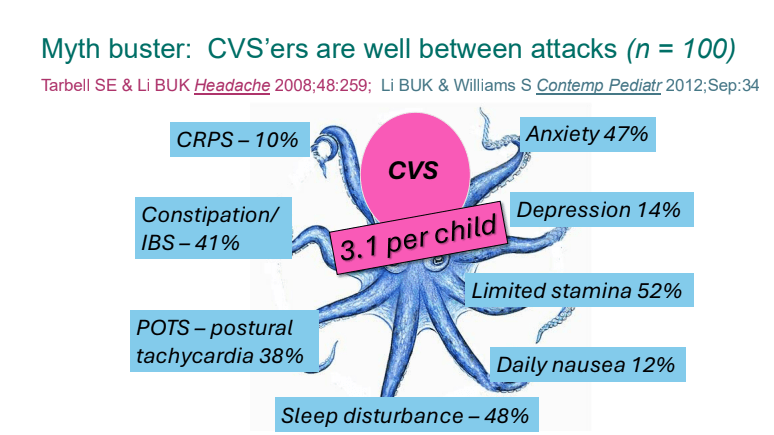
- Previously, CVS patients were thought to be well in between episodes. However, ~40% have inter-episode symptoms
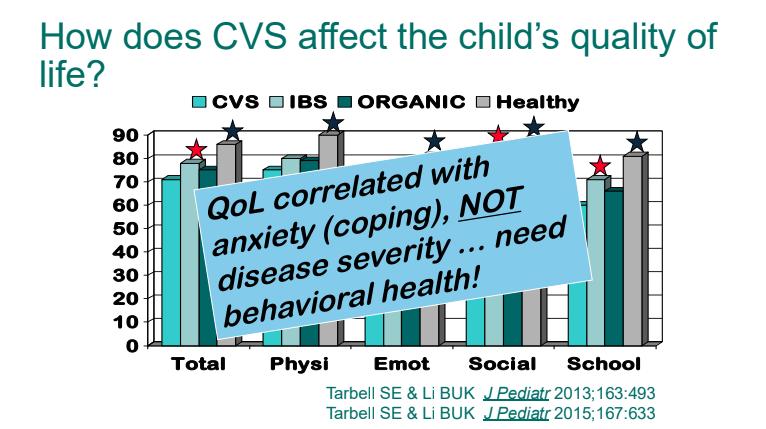
- Quality of life is correlated mainly with anxiety/coping rather than the severity of episodes
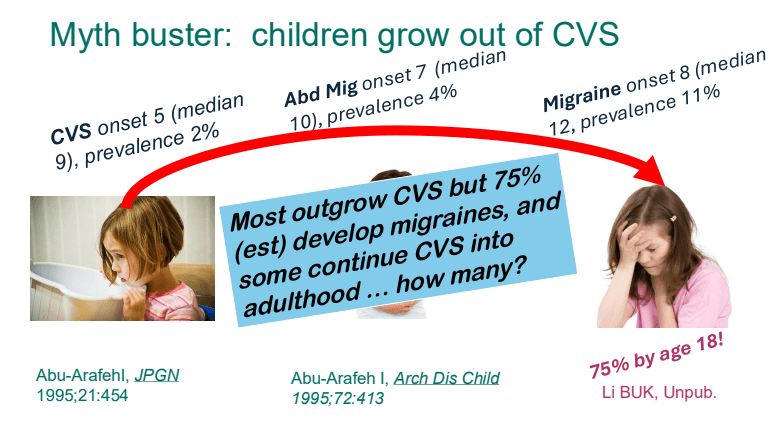
- Children with CVS often (~75%) develop migraines by adulthood
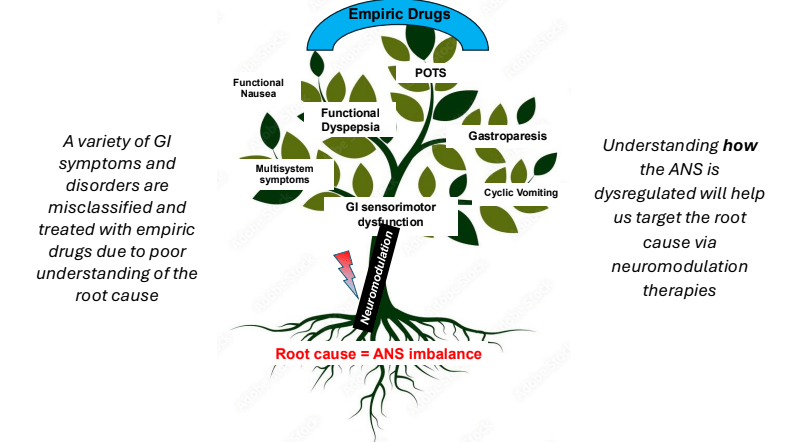
- Underlying pathophysiology likely involves the autonomic nervous system

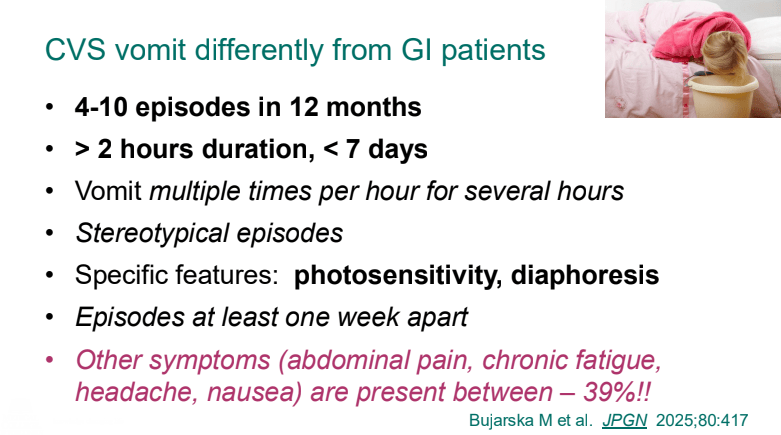
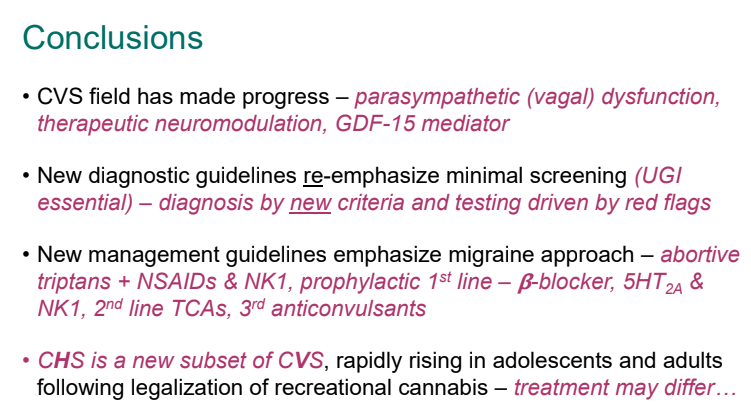
- 2025 CVS Guidelines — took about 3 years to develop. It is noted that the 2008 guideline diagnostic criteria missed about 48% of cases (Bujarska et al. JPGN 2025; 80: 417)
- 2025 Guidelines emphasize limited diagnostic workup at presentation (eg. UGI and basic labs) unless there are alarm symptoms. Alarm symptoms include the following:


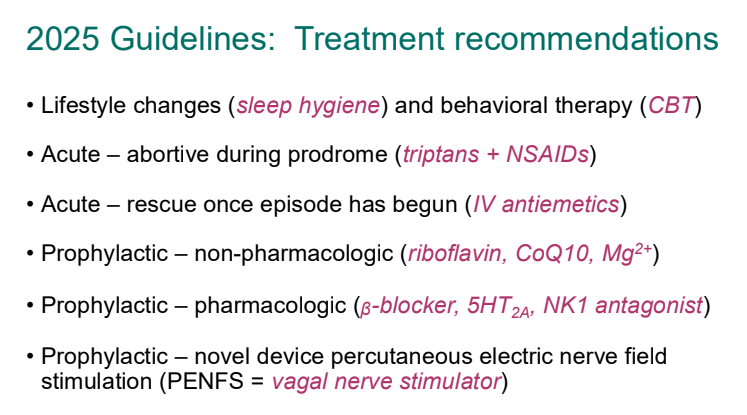
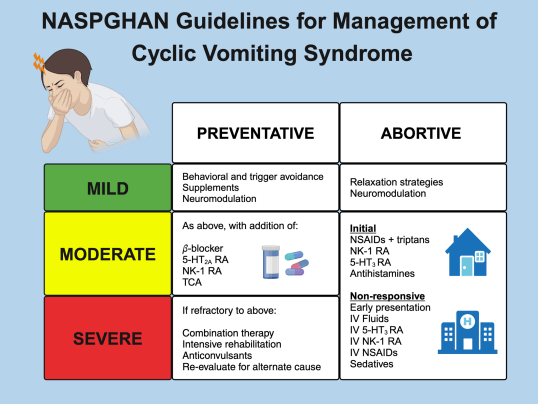
- For abortive therapy, the new guidelines favor aprepitant over ondansetron, and generally favor D5 over D10 IVFs.
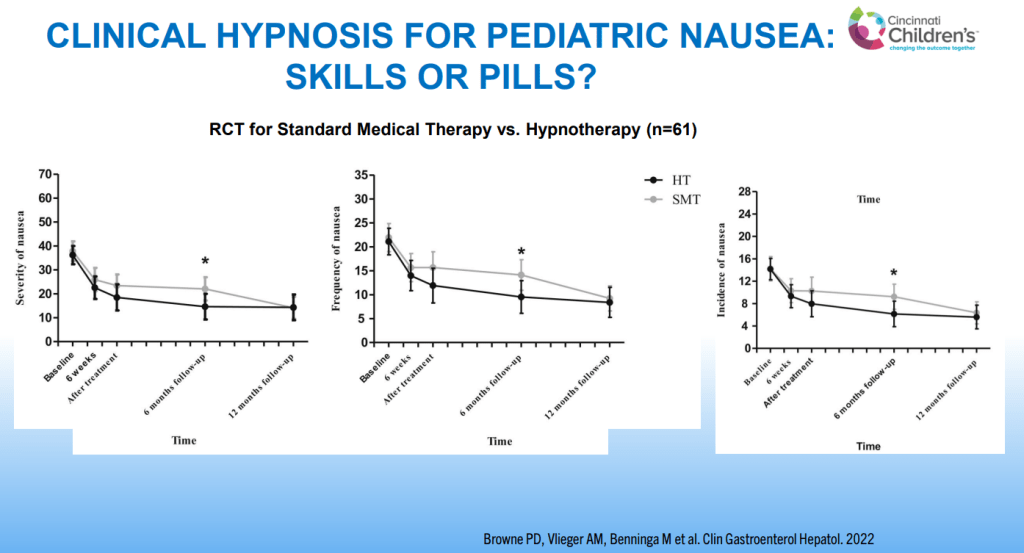
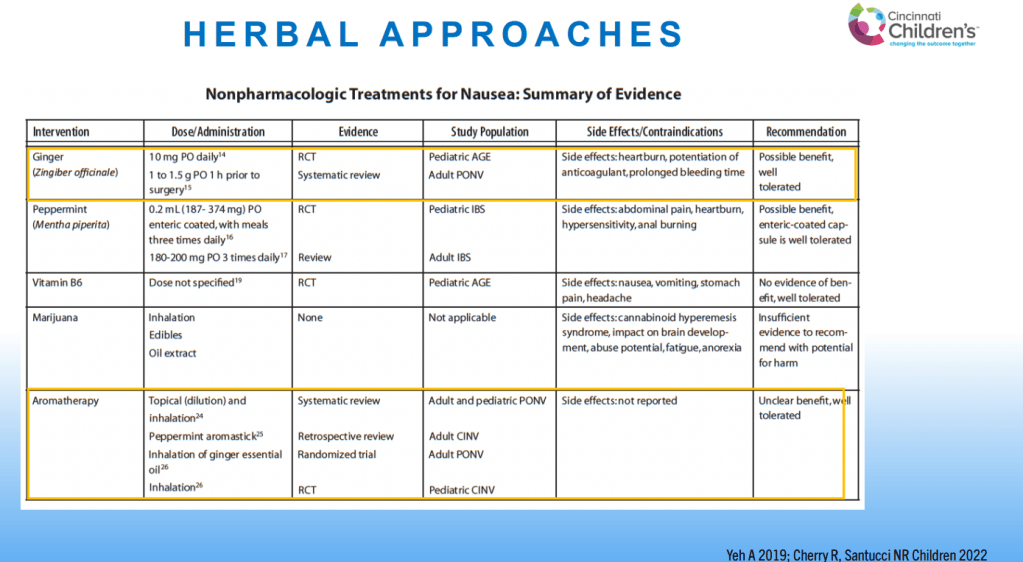
- For prophylactic therapy, there is now an emphasis on non-pharmacologic therapy in addition to pharmacologic agents and PENFS. Propranolol and aprepitant are favored prior to use of TCA agents like amitriptyline due to side effect profile
- Action plan for ED may help speed care and lower likelihood of admission
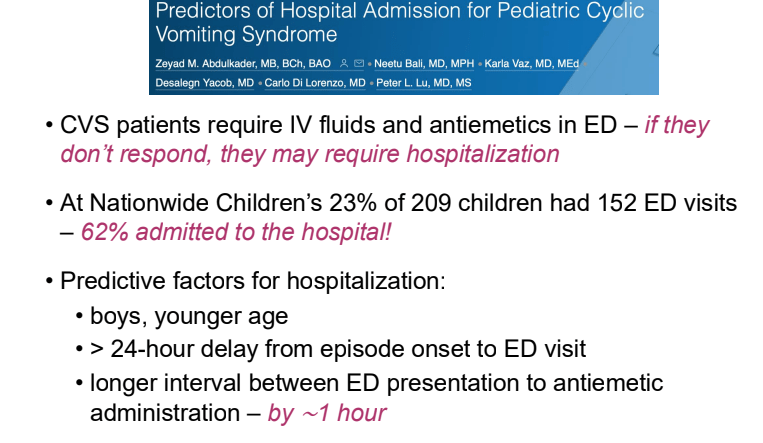

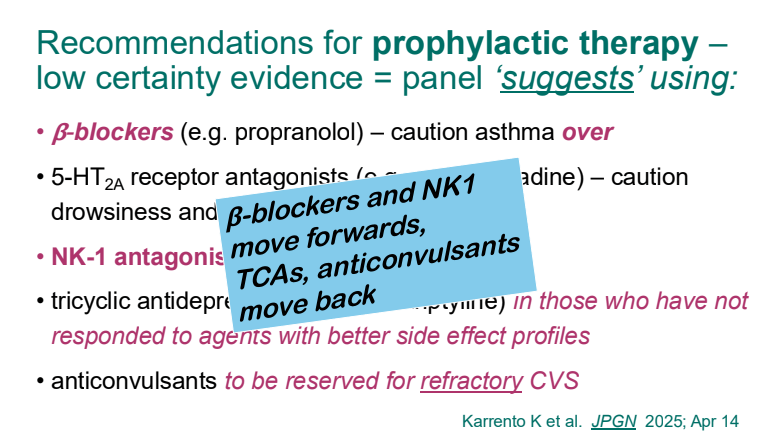
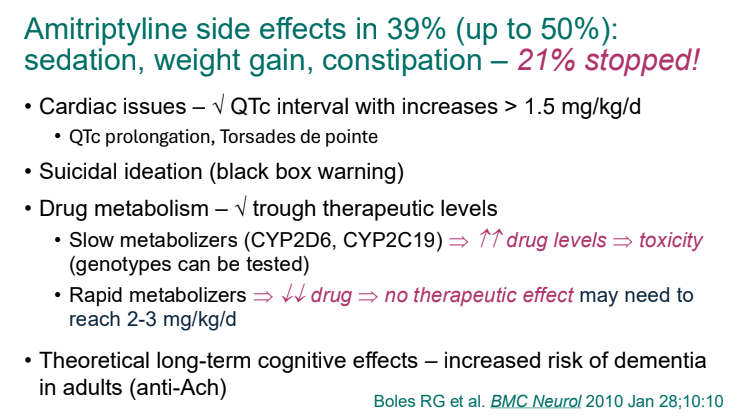
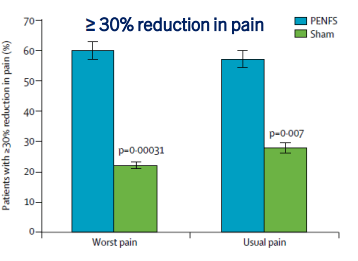
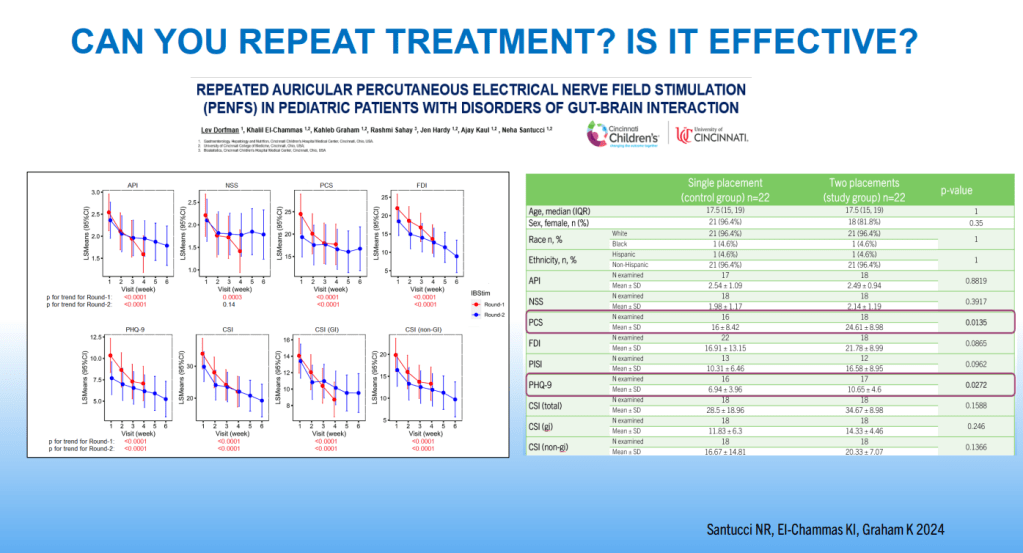
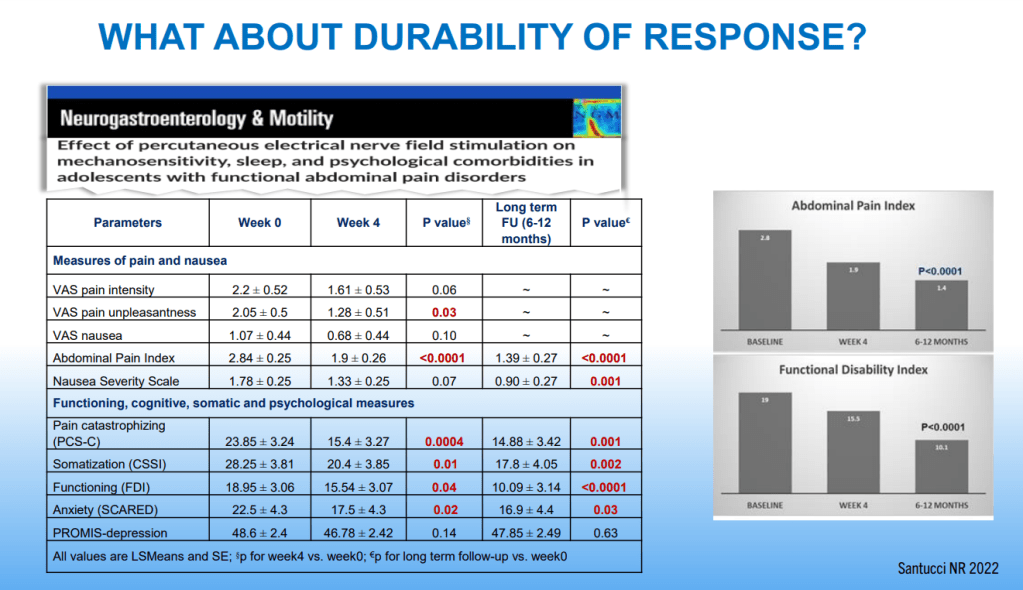
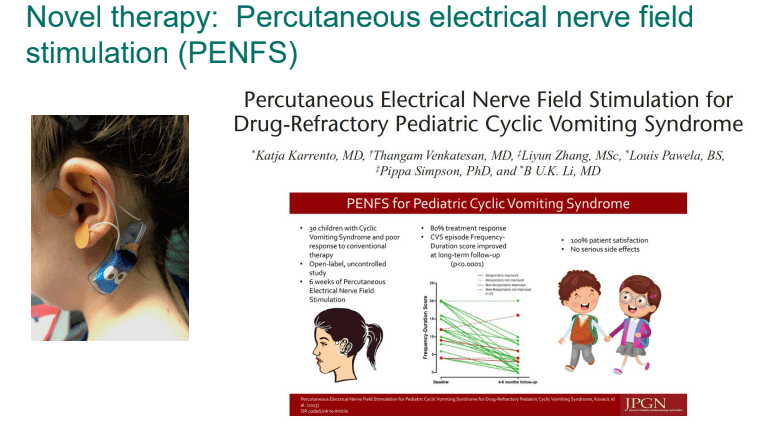
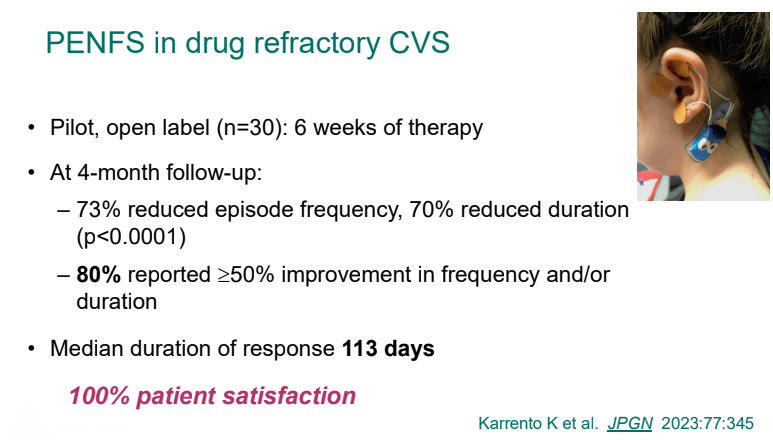
- PENFS for prophylactic therapy had a durable response (113 days) in a recent study
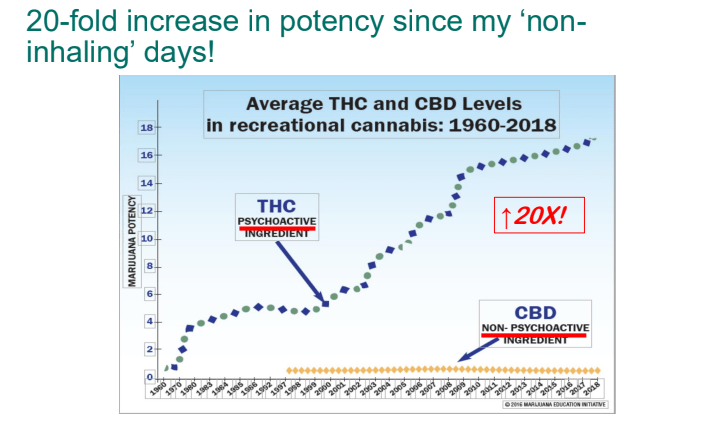
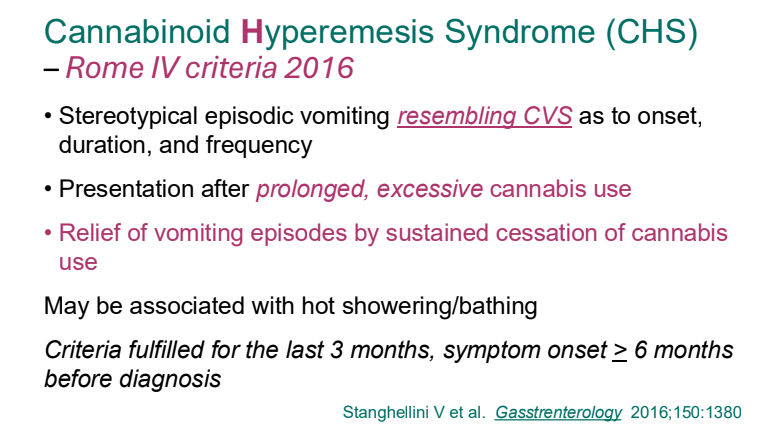
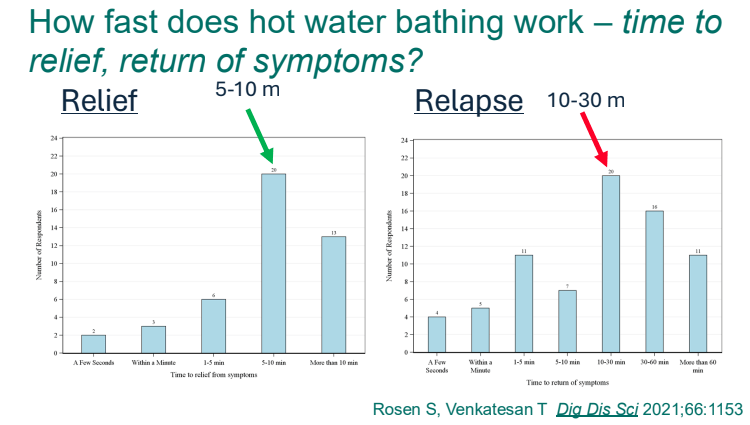
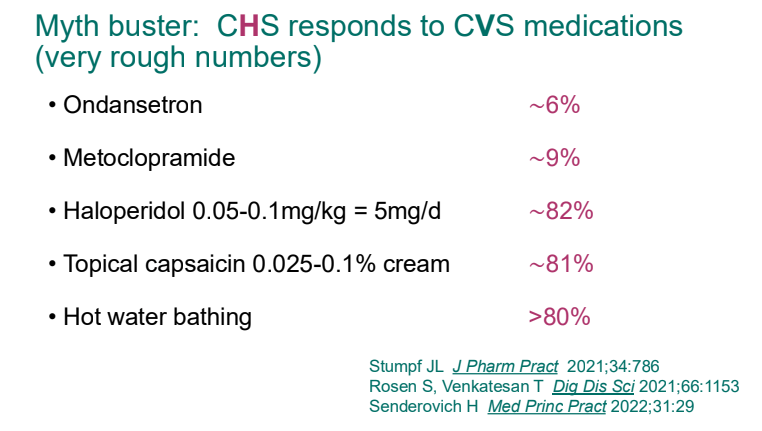
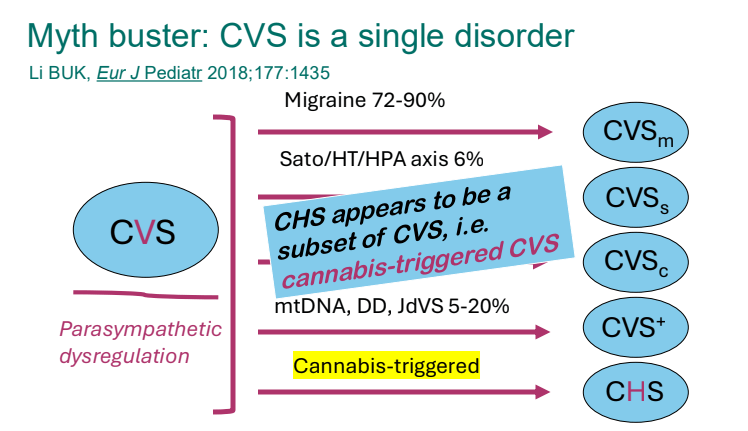
- Cannaboid hyperemesis syndrome (CHS) was first described in 2004 and has been rapidly increasing related to increased use and potency of THC products. Haloperidol, topical capsaicin and hot water (prolonged) bathing are often effective

Related blog posts:
- 2025 Pediatric Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome Guidelines
- Cyclic Vomiting ED Protocol
- Abraham Lincoln’s Cyclic Vomiting Action Plan (the authors’ of the article chose to list the patient’s name a Abraham Lincolon on their action plan)
- Diet or Drugs for Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- Aprepitant for CVS
- Neuro-Stim for Refractory Cyclic Vomiting?
- Costs/Yield of Diagnosing Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- How to Distinguish Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome and Cannabis Hyperemesis Syndrome
- Topiramate -2nd Line Agent for Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- Misdirection: False-positive Urine Cannaboid Screen due to Pantoprazole | gutsandgrowth
Disclaimer: This blog, gutsandgrowth, assumes no responsibility for any use or operation of any method, product, instruction, concept or idea contained in the material herein or for any injury or damage to persons or property (whether products liability, negligence or otherwise) resulting from such use or operation. These blog posts are for educational purposes only. Specific dosing of medications (along with potential adverse effects) should be confirmed by prescribing physician. Because of rapid advances in the medical sciences, the gutsandgrowth blog cautions that independent verification should be made of diagnosis and drug dosages. The reader is solely responsible for the conduct of any suggested test or procedure. This content is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a condition