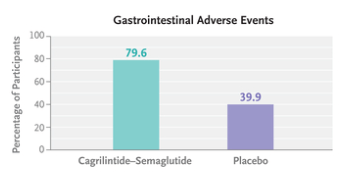
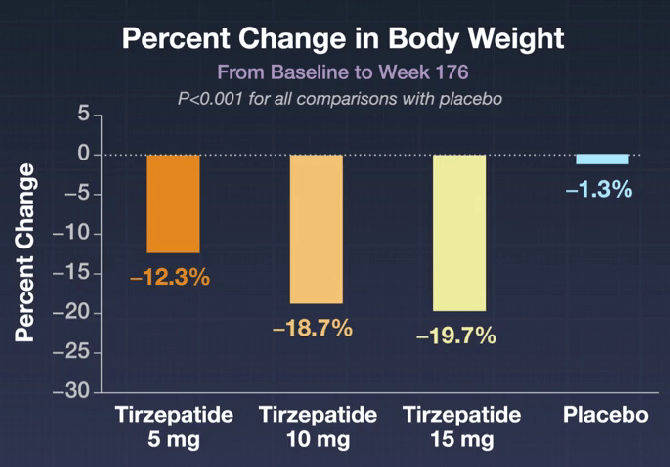
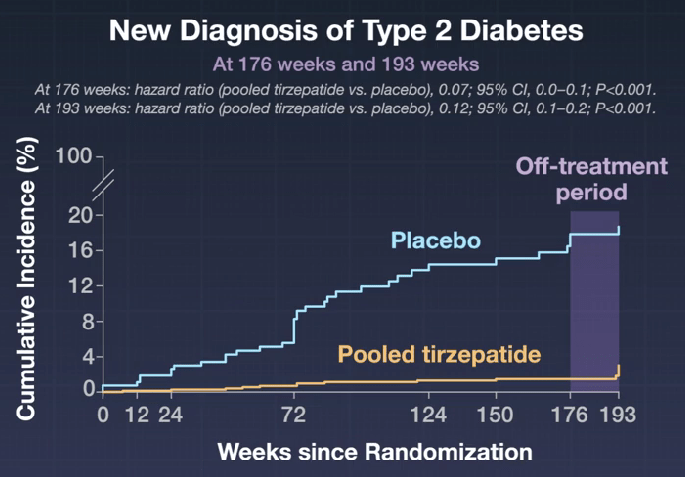
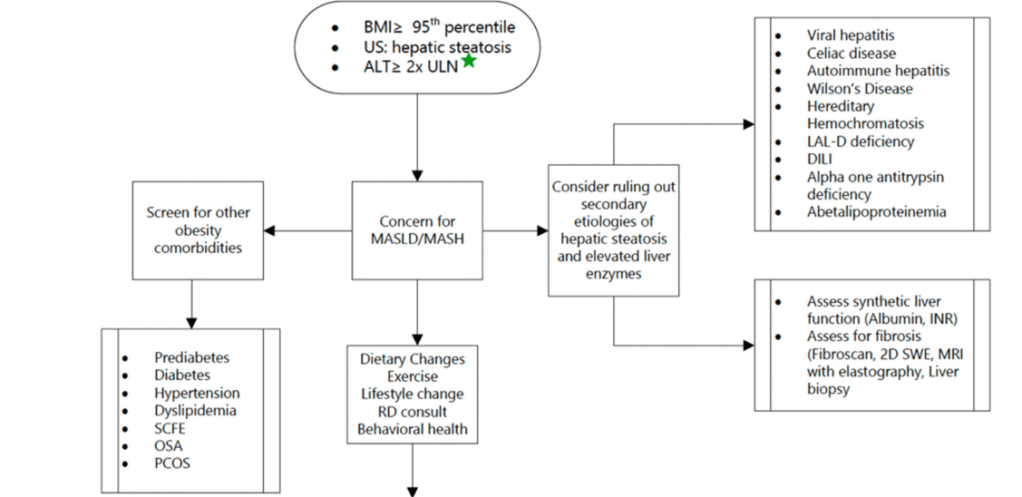
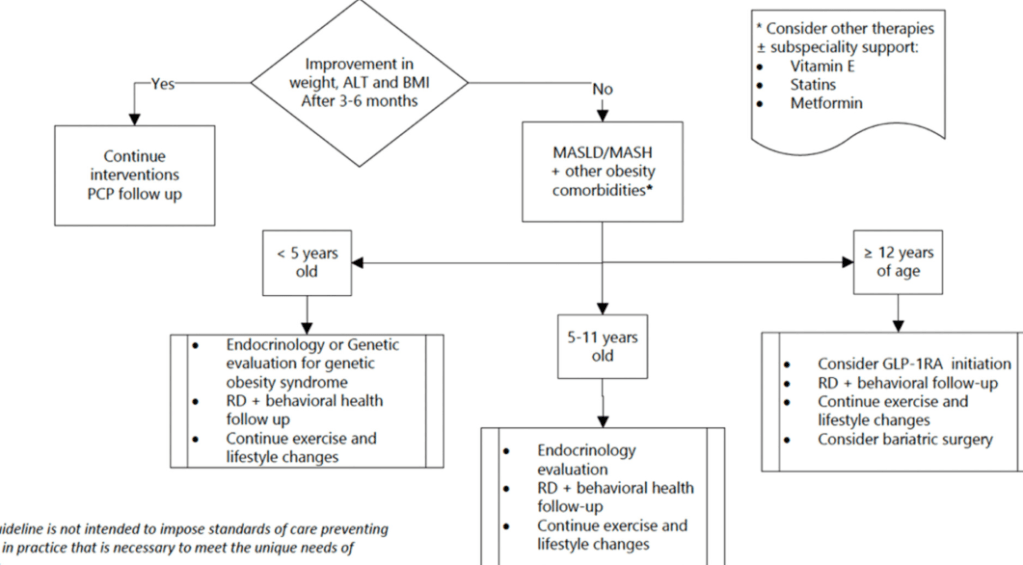
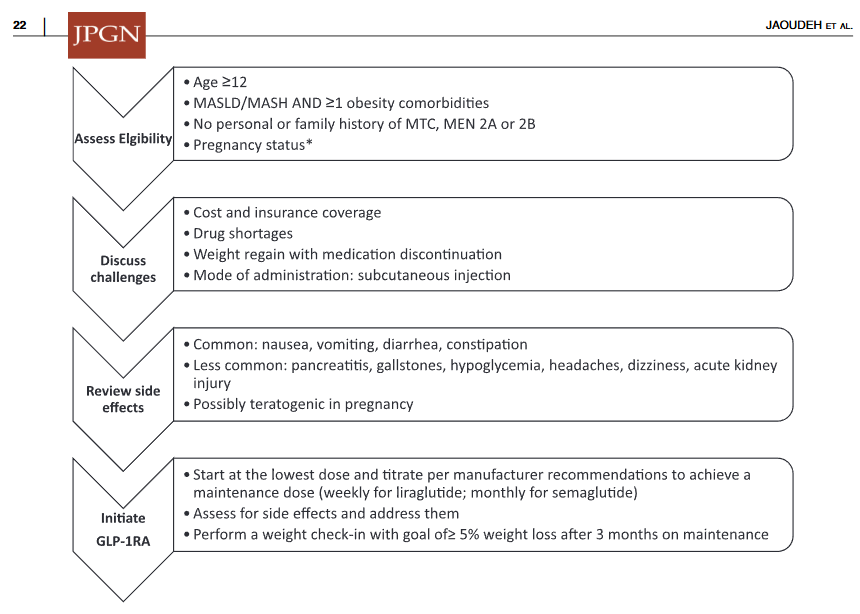
AM Tou, J Panganibanl. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025; DOI: 10.1002/jpn3.70242. Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists in pediatric metabolic dysfunction‐associated steatotic liver disease
Background: “Recent seminal studies such as the ESSENCE trial have demonstrated MASH resolution with improvement in fibrosis in adult patients with biopsy-proven steatohepatitis treated with semaglutide.18 This has led to the pivotal FDA approval of semaglutide for the treatment of MASH in adults.”
Methods: 42 patients with MASLD (see study for details). 71% of patients had a therapeutic indication for T2DM and 29% for obesity. Of the GLP-1RA medications, liraglutide was most frequently prescribed (44%), followed by semaglutide (27%), dulaglutide (25%), and exenatide (4%).
Key findings:
- ALT improved by a mean of 56 U/L at 6 months (p = 0.04), and by 37 U/L at en-of-treatment (p = 0.004).
- GLP-1RA use was associated with significant improvements in alanine transaminase (ALT) along with other cardiometabolic biomarkers even in the absence of improvements in body mass index percentile or z-score. There were reductions in GGT, AST, triglycerides, and HbA1C
- In this study, there was not a significant decline in weight. Prior studies have shown less weight loss in patients with T2DM compared to those with obesity (w/o T2DM)
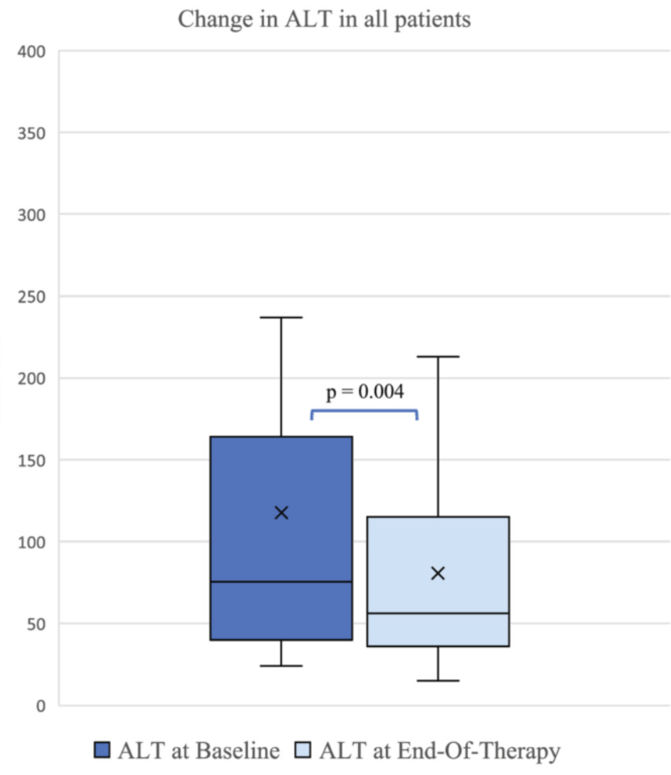
My take: It is helpful to have a pediatric study that shows that GLP1-RAs are effective specifically in those with MASLD.
Related blog posts:
- Pharmacological Management of Pediatric Steatotic Liver Disease (2025)
- FDA Approves Semaglutide for MASH
- Semaglutide’s Efficacy in Phase 3 MASH Trial
- Semaglutide in Adolescent Obesity
- Diets for Obesity and Steatotic Liver Disease Plus Patient Information from FISPGHAN
- GLP-1 Obesity Medication for 6-11 Year Olds