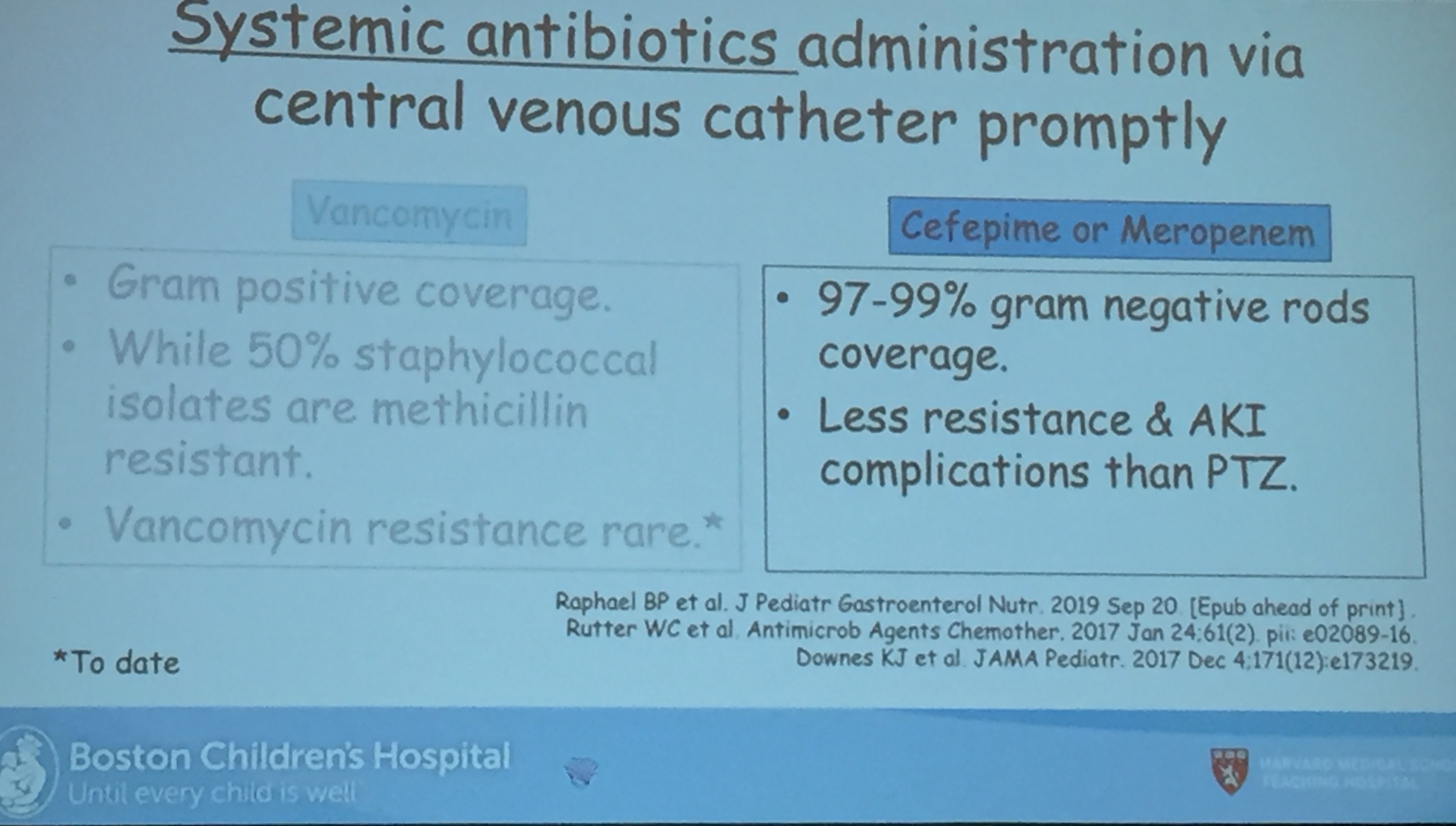
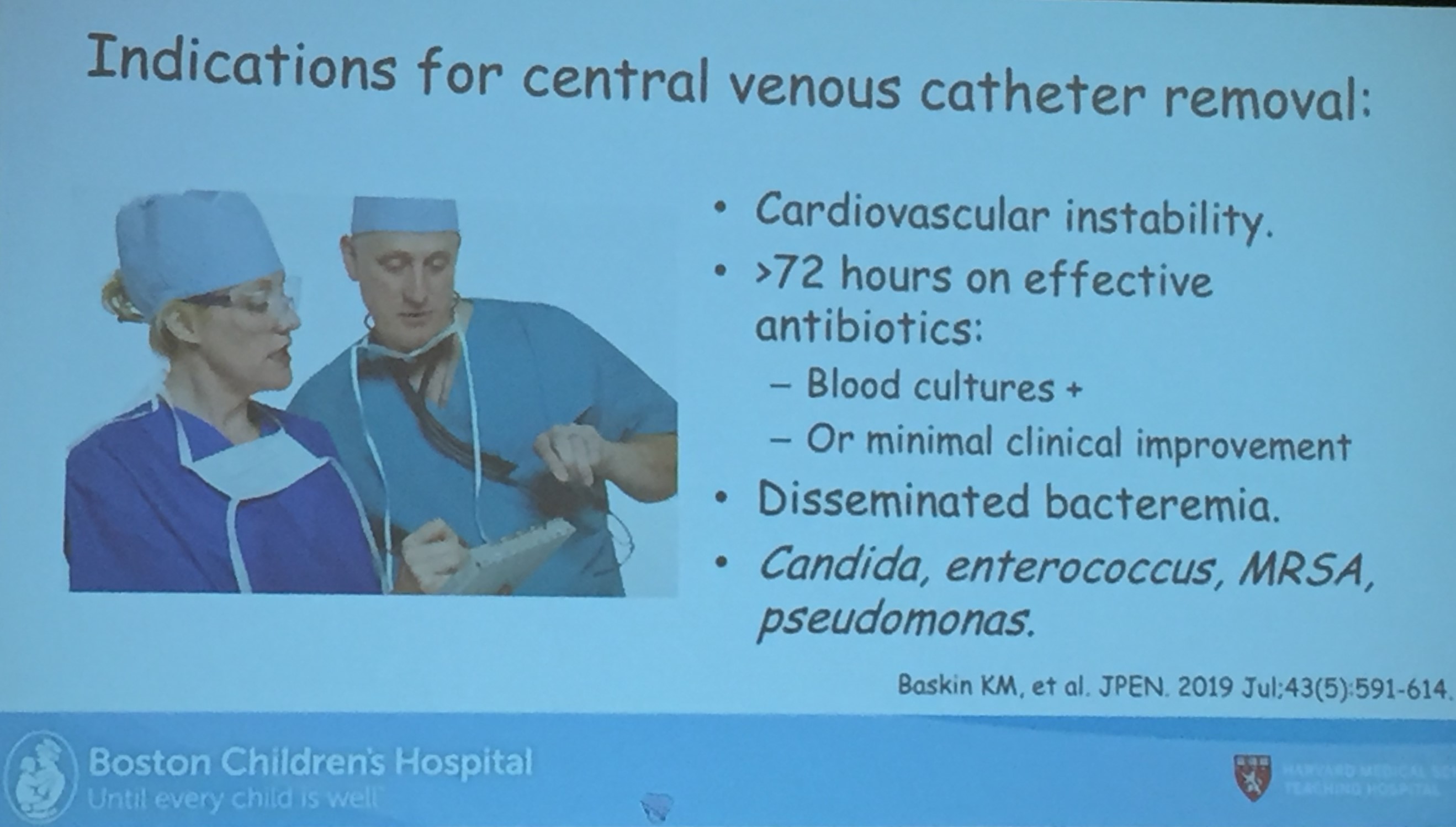
J Hilberath et al. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2025;81:736–742. Open Access! Post‐endoscopic fever and infection in paediatricpatients with intestinal failure
Methods: This was a retrospective single-center observational study which included children with IF and CVC who underwent GI endoscopy between 2019 and 2024. Intravenous antibiotic prophylaxis was used in 71.2% of the procedures.
Key findings:
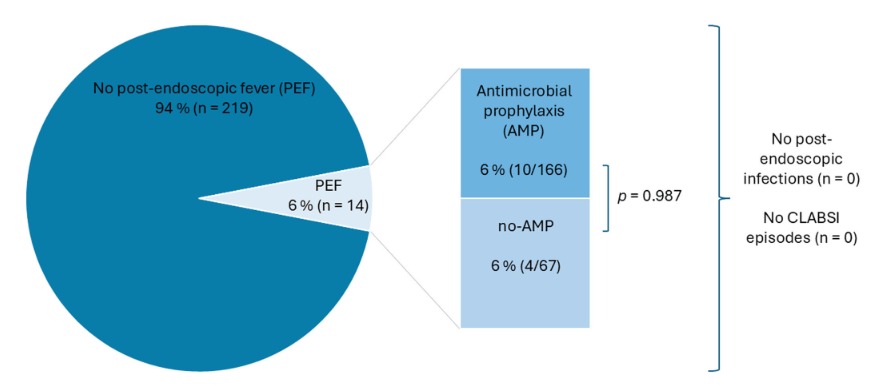
- The overall post-endoscopic fever (PEF) rate was 6%, with no significant difference between the group that received prophylactic antibiotics and the group that did not. Specifically, there were 10 with PEF that had received prophylactic antibiotics and 4 that had PEF with no prophylaxis
- No infections, including central line-associated bloodstream infections, were observed
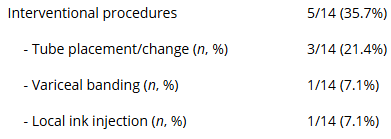
- 5/14 of the cases with PEF had an interventional procedure. The remainder had a diagnostic EGD, colonoscopy or both.
Interventional Cases:
Discussion Points:
- “PEF in children with IF was 6%, which is approximately 10 times higher than the recently published 0.55% in pediatric patients following endoscopic procedures by Boster et al.” (see: Must-Read: How to Handle Post-Procedure Fevers)
- A strength of this study was that the comparison of children with IV antibiotics versus those without was due to an institutional policy change in 2022. This helps eliminate selection bias in the determination that IV antibiotics were not beneficial in preventing PEF
My take: The high rate (6%) of PEF should be discussed with families prior to endoscopic procedures. The rate was increased (36%) in those with interventional procedures. It is reassuring that no definitive infections were identified despite the fevers.
Related blog post: Must-Read: How to Handle Post-Procedure Fevers