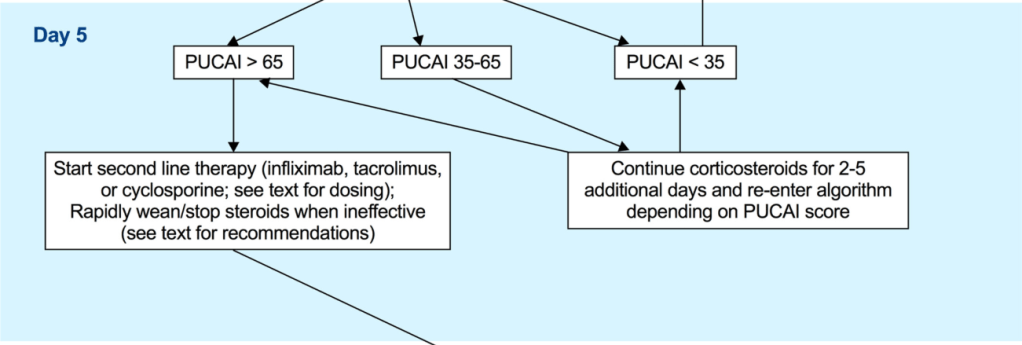
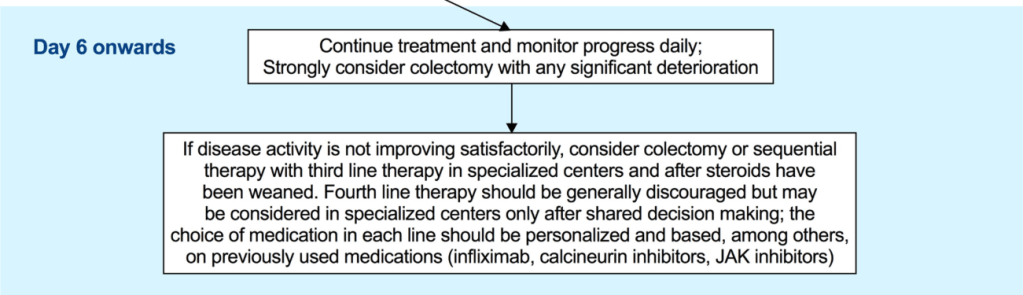
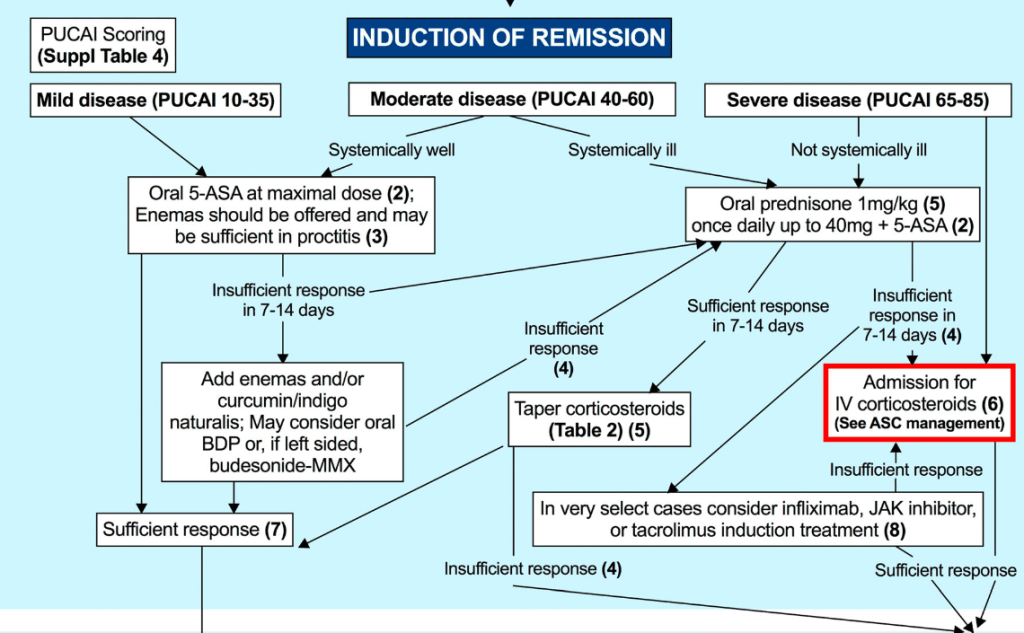
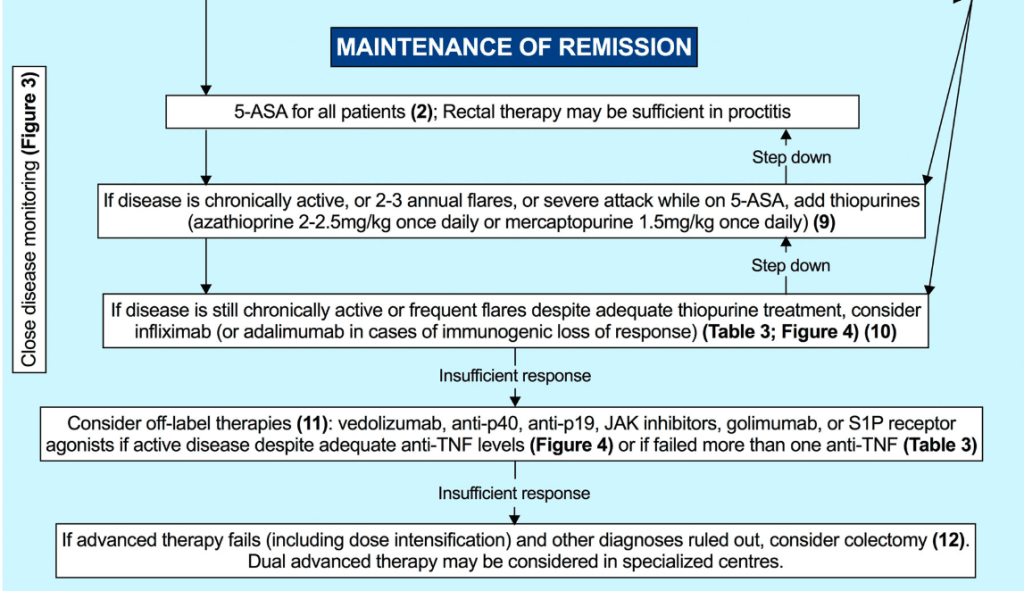
Y Frutkoff et al. Gastroenterology 2025 (Article in Press). Open Access! Whole Food Diet Induces Remission in Children and Young Adults With Mild to Moderate Crohn’s Disease and Is More Tolerable Than Exclusive Enteral Nutrition: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Yesterday’s post (“A Practical Guide to Diet and IBD” (2025)) provided a summary of data on a multitude of diets for inflammatory bowel disease. Today’s post describes a study on a new diet, called the Tasty & Healthy diet.
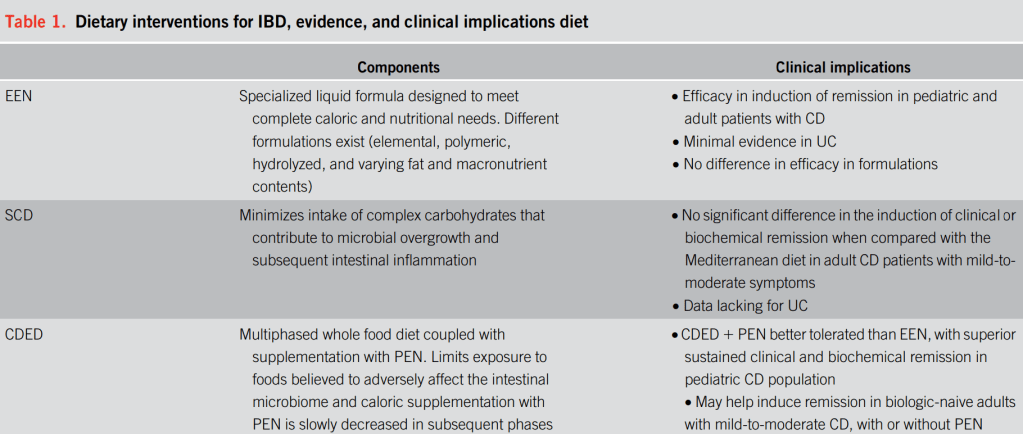
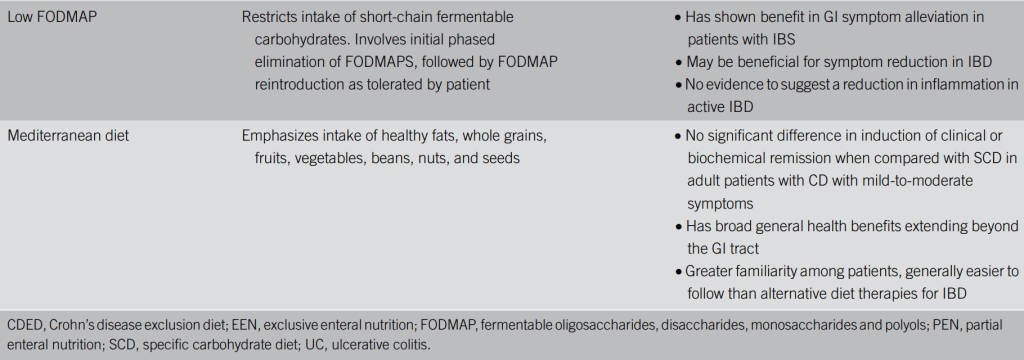
Background: Tasty & Healthy (T&H) is a whole food diet for Crohn’s disease (CD) that excludes processed food, gluten, red meat, and dairy, without requiring formula or mandatory ingredients.
Tasty & Healthy (T&H) is an exclusive whole food diet, first published in a charity cookbook in 2014… The T&H diet was developed to reduce proinflammatory dietary exposures by excluding gluten, animal fat (ie, red meat and dairy, except for plain yogurt), as well as all processed food (anything that comes in a package except for those with 1 unprocessed ingredient.” (see details and supportive references in Supplementary Appendix 1).
Methods: TASTI-MM was a clinician-blinded, randomized controlled trial comparing tolerability and effectiveness of T&H (n=41) vs exclusive enteral nutrition (EEN, n=42). The intention to treat analysis included 83 patients (mean age 14.5 yrs, range 7-25 yrs).
Key findings:
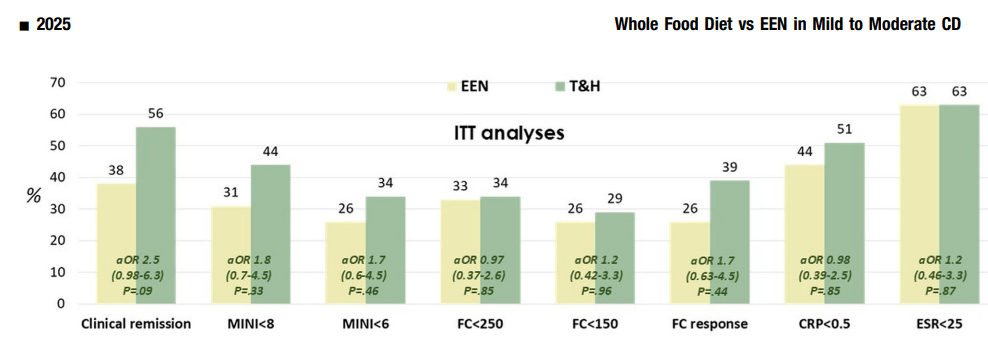
- 88% tolerated T&H vs 52% for EEN. 59% of the patients in the EEN arm did not complete the 8-week follow-up period, compared with only 15% in the T&H arm
- Calprotectin, C-reactive protein, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate decreased significantly in both groups, with no between-group differences
- Symptomatic remission was achieved in 56% of the T&H group vs 38% of the EEN group
- Calprotectin <250 μg/g was achieved in 34% T&H vs 33% of the EEN group
- Microbiome α-diversity improved in the T&H arm and declined in the EEN arm, showing superior species richness at both week 4 and week 8. Species associated with bowel inflammation, such as Ruminococcus gnavus, decreased in T&H and increased in EEN (q < .001)
Discussion Points:
“In multiple studies CDED has been found to induce symptomatic remission in 62%–77% of patients with mild to moderate uncomplicated CD, including biologic remission in a subset of patients. Although conceptually similar to CDED in the exclusion of proinflammatory food
groups, the T&H diet differs in structure—requiring no formula and no mandatory components, thus offering greater dietary flexibility.”
“The T&H diet was tested across multiple international centers, while still achieving similar outcomes compared with EEN. The use of any exclusion diet requires guidance of a dietitian to ensure balanced nutrition, and this becomes even more important in diets when formula is not needed. Other exclusive whole food diets studied in the RCT setting are the Specific Carbohydrate Diet and Mediterranean diet, which were effective in inducing symptomatic remission, but demonstrated insufficient biologic remission rates.”
“In the past, dietary interventions have not been as widely adopted in adults as in children…Although EEN use has been hampered by the thought that adults will not tolerate nutritional interventions, the advent of whole food diets has changed that notion…In this study, we found that not only were the included adults adherent to the T&H diet, it was as effective as in children and treatment response was not associated with age.”
Related article: Plotkin L, Aharoni Y, Fenster D, et al. Tasty & Healthy is a
dietary approach for inducing and maintaining remission in Crohn’s disease: a prospective case series. United European Gastroenterol J 2021;9:521 (PO431).
My take: This “Tasty & Healthy” Diet appears to be an effective option for induction of remission for mild to moderate Crohn’s disease. Extended studies will be needed to help determine whether it could be used for longer duration in those with a response. Also, whoever labelled this diet initially clearly understands marketing as it sounds a lot better than EEN or CDED.
Related blog posts:
- AGA Guidance: Nutritional Therapies for Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- The Quality of Evidence for Dietary Treatments in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- CDED + PEN: An Alternative Diet to Exclusive Enteral Nutrition?
- Dr. Maria Oliva-Hemker: Positioning Therapies for Pediatric Crohn’s Disease
- More Evidence That A Proinflammatory Diet May Increase the Risk of Crohn’s Disease
- Pushing the Boundaries on Dietary Therapy for Crohn’s Disease (CD-TREAT)
- Predicting Enteral Nutrition Therapy Response in Patients with IBD
- Dietary Therapy for Adults with Crohn’s Disease
- Trial by Diet Approach for Crohn’s Disease in Children
- Dietary Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease –Useful Update
- Mediterranean Diet vs Specific Carbohydrate Diet for Crohn’s Disease
- Mediterranean Diet’s Impact on Crohn’s Disease Outcomes
Disclaimer: This blog, gutsandgrowth, assumes no responsibility for any use or operation of any method, product, instruction, concept or idea contained in the material herein or for any injury or damage to persons or property (whether products liability, negligence or otherwise) resulting from such use or operation. These blog posts are for educational purposes only. Specific dosing of medications (along with potential adverse effects) should be confirmed by prescribing physician. Because of rapid advances in the medical sciences, the gutsandgrowth blog cautions that independent verification should be made of diagnosis and drug dosages. The reader is solely responsible for the conduct of any suggested test or procedure. This content is not a substitute for medical advice, diagnosis or treatment provided by a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a condition