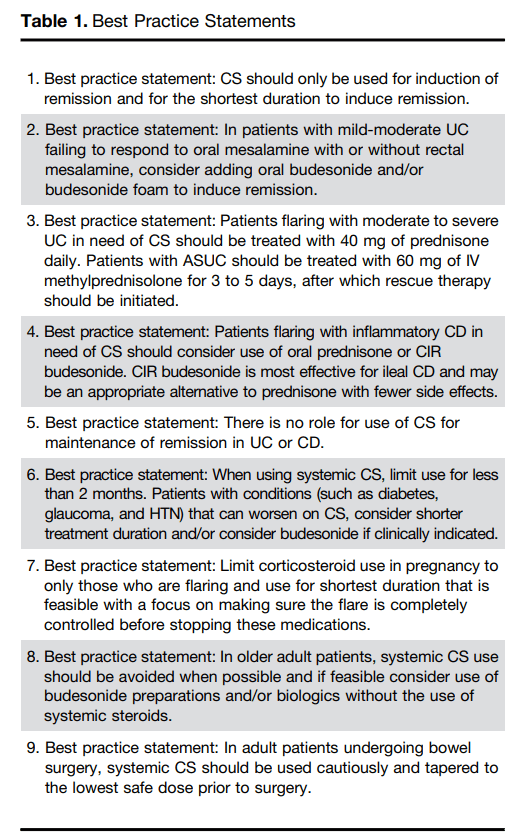
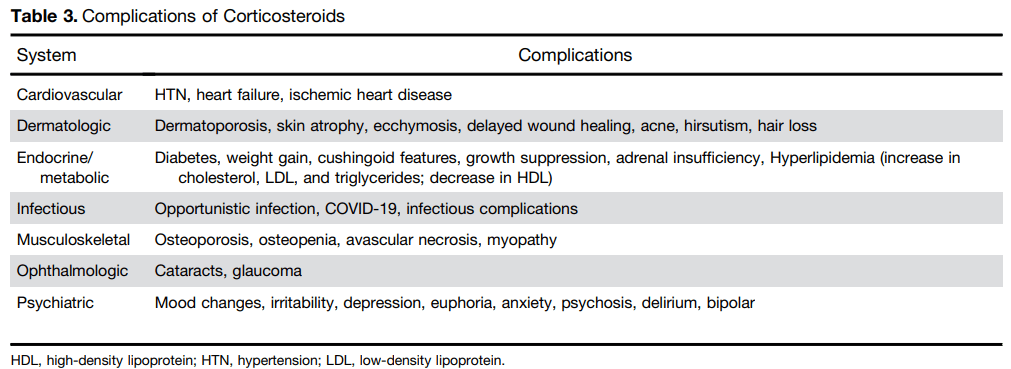
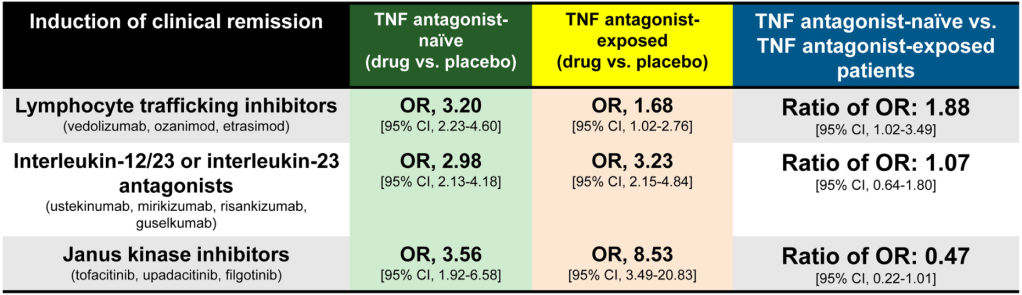
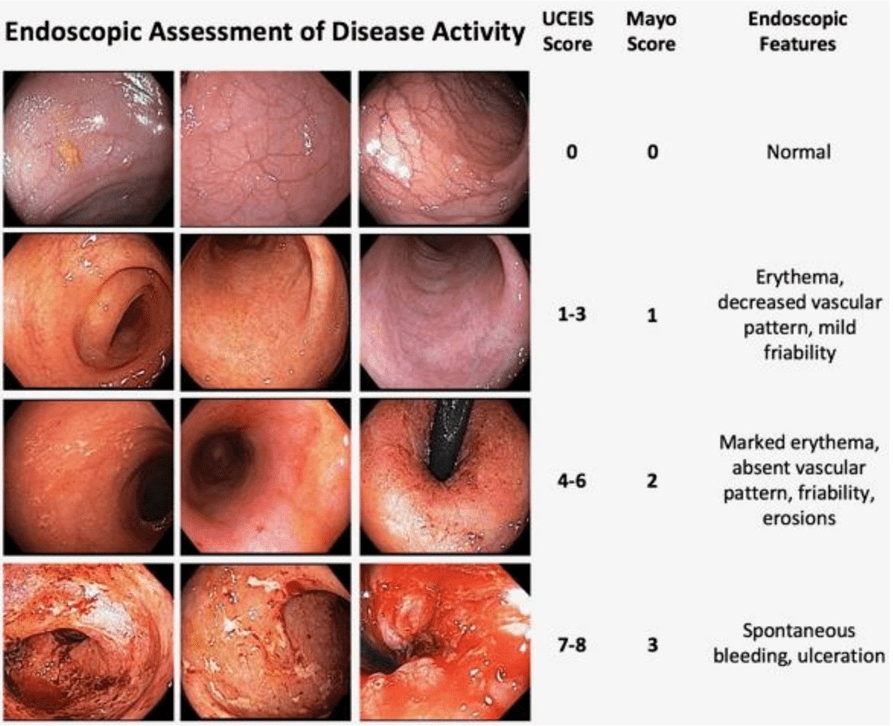
C Larson et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2025; 23: 2263-2271. Postoperative Outcomes in Tofacitinib-Treated Patients With Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Undergoing Colectomy
This was a multicenter, retrospective, case-control study of patients hospitalized with ASUC who underwent colectomy, comparing patients treated with tofacitinib (n=41) prior to colectomy with infliximab-treated controls (n=68).
Key findings:
- Compared with tofacitinib-treated patients, infliximab-treated patients had higher overall rates of overall (44 [64.7%] vs 13 [31.7%]; P = .002) and serious (19 [27.9%] vs 3 [12%]; P = .019) postoperative complications
My take: This study supports the safety of JAK inhibitor therapy for ASUC. It showed a significantly lower rate of overall postoperative complications in ASUC patients treated with tofacitinib compared with infliximab; the authors note that “these findings can likely be extrapolated to upadacitinib, a selective JAK inhibitor, given its similar mechanism of action.”
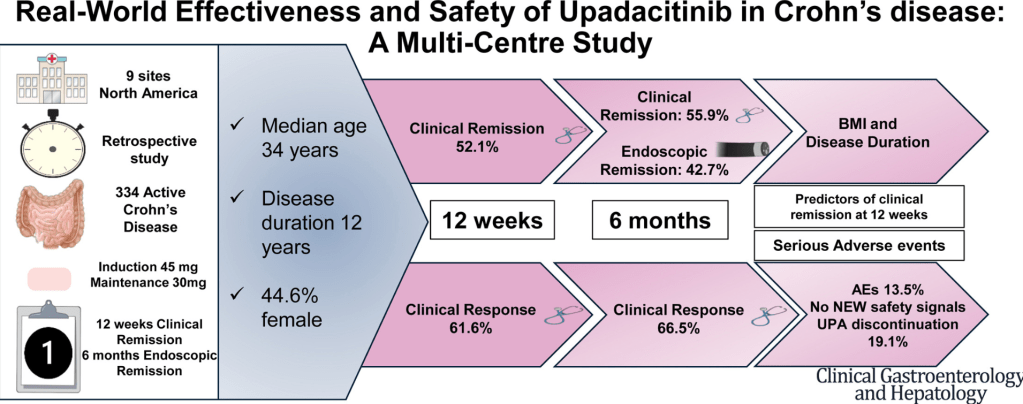
J Devi et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2025; 23: 2281-2291. Open Access! Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Upadacitinib in Crohn’s Disease: A Multicenter Study
Related blog posts:
- Safety of JAK Inhibitors Compared to Anti-TNF Agents
- Prior Exposure to TNF Antagonists May Increase Response to JAK Inhibitors in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis
- Tofacitinib Outperformed Vedolizumab in Anti-TNF-experienced Ulcerative Colitis
- Treatments for “Bad” Inflammatory Bowel Disease (Part 2) & Reassuring Data on Tofacitinib
- Upadacitinib for Crohn’s Disease: U-ENDURE Study
- Upadacitinib’s Effectiveness for Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease
- IBD Briefs: Upadacitinib in Children, Predicting Crohn’s Disease, and Autoimmune Diseases Associated with IBD
- How Quickly Does Upadacitinib Work for Crohn’s Disease Symptoms?
- Landmark Study: Oral Biologic for Crohn’s –Upadacitinib