U Mahadevan et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2025 (published ahead of print). Open Access! Global Consensus Statement on the Management of Pregnancy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Addendum -updated reference: U Mahadevan et al. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2025; 23: S1-S60. Open Access! Global Consensus Statement on the Management of Pregnancy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease
This is a 60 page open access article. Table 1 lists 34 “GRADE” statements and Table 2 lists 35 consensus statements. This article is also jointly published in the following:
- Gut
- Am J Gastroenterol
- Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
- Journal of Crohn’s and Colitis
- Aliment Pharmacol Ther
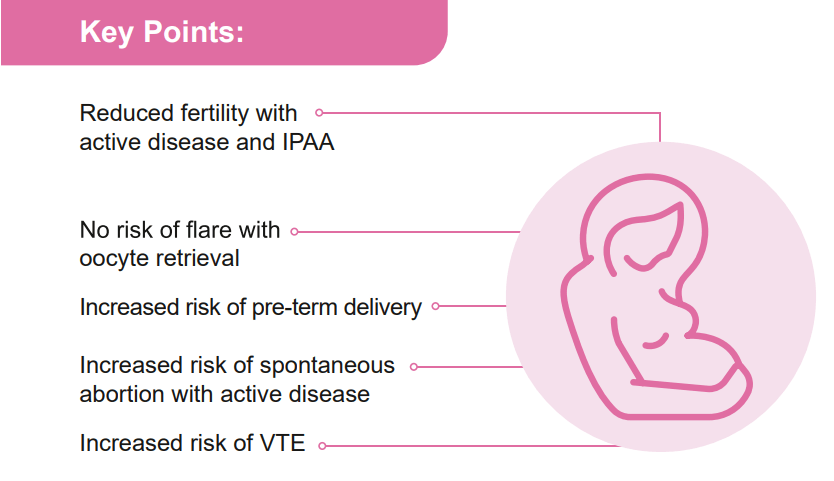
For Moms:

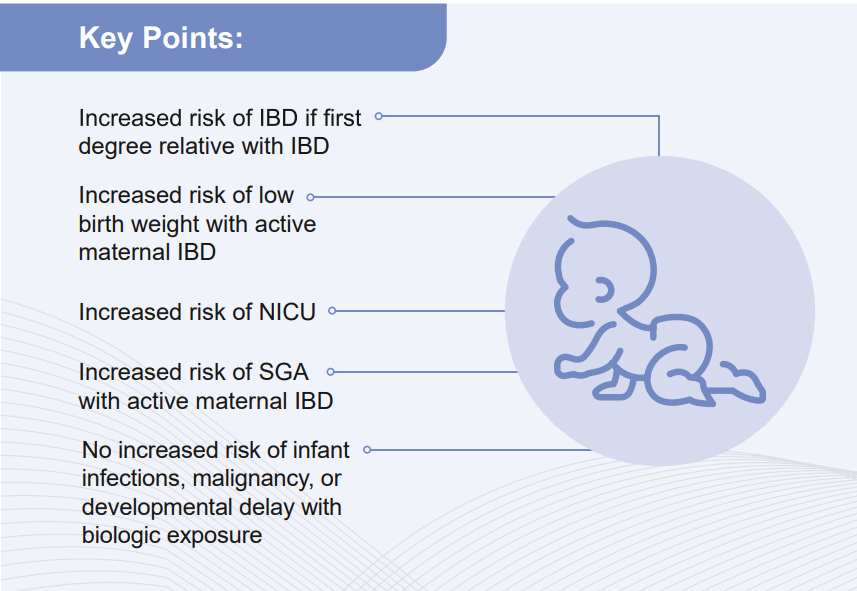
For Babies:
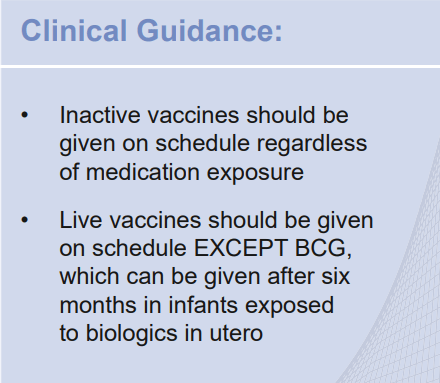
My take: This is a useful reference –mainly helpful for gastroenterologists rather than pediatric providers.
Related blog posts:
- IBD Shorts: High TNF levels, Biologics in Pregnancy, & Ileocolic Resection Outcomes in Pediatrics
- IBD Updates: Outcomes of VEO-IBD, PIANO Study Update, and Insurance-Disparity Relationship (2021)
- Disease Activity, Not Medications, Linked to Neonatal Outcomes Among Women with IBD (2020)
- CCFA Conference Notes 2016 (part 4) –Pregnancy and IBD