Thus far, the relationship of the microbiome and inflammatory bowel disease has been a ‘chicken and the egg which came first’ conundrum. A new study (EC Brand, MAY Klaassen et al. Gastroenterol 2021; 160: 1970-1985. Full text pdf: Healthy Cotwins Share Gut Microbiome Signatures With Their Inflammatory Bowel Disease Twins and Unrelated Patients) offers some insight into this issue.
Methods: Fecal samples were obtained from 99 twins (belonging to 51 twin pairs), 495 healthy age-, sex-, and body mass index–matched controls, and 99 unrelated patients with IBD. Whole-genome metagenomic shotgun sequencing was performed.
Key findings:
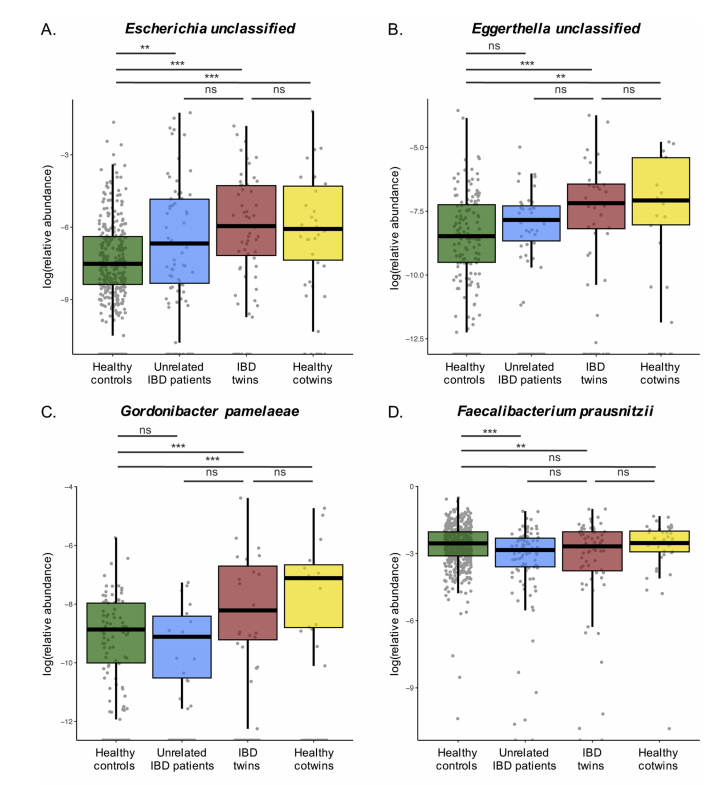
- No significant differences were observed in the relative abundance of species and pathways between healthy cotwins and their IBD-twins.
- Compared with healthy controls, 13, 19, and 18 species, and 78, 105, and 153 pathways were found to be differentially abundant in healthy cotwins, IBD-twins, and unrelated patients with IBD, respectively.
Discussion: “The gut microbiome composition of individuals at increased risk of developing IBD (i.e. healthy cotwins from IBD-discordant twin pairs) displays IBD-like signatures on a species and pathway level…The overlap in gut microbial features between healthy cotwins at increased risk of developing IBD and related and unrelated IBD patients suggests that these IBD-like microbiome signatures might precede the onset of IBD. This potentially opens new avenues for diagnosis and therapy in individuals with pre-symptomatic IBD.”
My take This study indicates that the microbiome changes in persons with IBD are also found in their healthy twins. In many ways, this is similar to the frequent finding of abnormal serology in Crohn’s disease; ASCA antibodies were considered much less helpful as a diagnostic test after the realization that ~20% of healthy first degree relatives also have detectable levels.
Figure 4 (pg 1979) shows the relative abundance of a selection of IBD-associated species and highlights similarities between the healthy cotwins and IBD twins.
Related blog posts:
- Gut Microbiome, Crohn’s Disease and Effect of Diet …
- Why Does Enteral Nutrition Work for Crohn’s Disease? Is it due to the Microbiome?
- Serology in IBD
- Dietary Therapy for Inflammatory Bowel Disease This is good lecture review on dietary therapy
- Good Food and Bad Food for Crohn’s Disease -No Agreement | gutsandgrowth
- Pushing the Boundaries on Dietary Therapy for Crohn’s Disease: CD-TREAT